The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining our overall health and well-being. This intricate network of vessels, nodes, and organs works tirelessly to protect us from infections and diseases. At the heart of this system are specialized cells that are responsible for carrying out the immune functions that keep us safe and healthy.
Lymphocytes
Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that are essential for the proper functioning of our immune system. There are two main types of lymphocytes: B cells and T cells. B cells produce antibodies that target and neutralize harmful pathogens, while T cells play a crucial role in coordinating the immune response and killing infected cells.
Macrophages
Macrophages are another important type of immune cell found within the lymphatic system. These cells are responsible for engulfing and digesting pathogens, dead cells, and debris. They also play a key role in presenting antigens to other immune cells, helping to initiate and regulate the immune response.
Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells are specialized antigen-presenting cells that play a critical role in activating the immune response. These cells are able to capture antigens from pathogens and present them to T cells, triggering an immune response. Dendritic cells are essential for recognizing and responding to foreign invaders, helping to protect the body from infections.
Natural Killer Cells
Natural killer cells are a type of lymphocyte that are able to recognize and destroy infected or cancerous cells. These cells play a crucial role in the body’s defense against tumors and viruses, helping to prevent the spread of disease throughout the body.
Summary
The lymphatic system is a complex network of vessels and organs that work together to protect the body from infections and diseases. Within this system, specialized cells such as lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and natural killer cells play key roles in carrying out immune functions. These cells work together to recognize and eliminate harmful pathogens, ensuring that our bodies remain healthy and free from disease.
Key Takeaways:
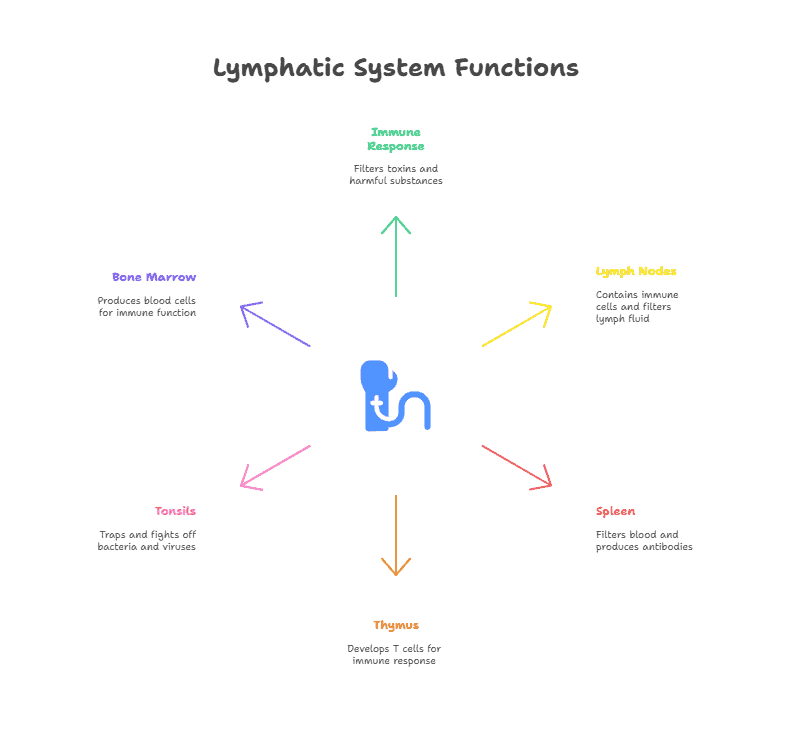
- The lymphatic system is a crucial part of the immune system, responsible for filtering and draining lymph fluid to remove toxins, waste, and pathogens from the body.
- Lymphocytes are a type of white blood cell that play a key role in the immune response, including B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells.
- The thymus gland is an important organ in the lymphatic system that produces and matures T cells, which are crucial for cell-mediated immunity.
- The spleen is another key organ in the lymphatic system that filters blood and helps to remove damaged or old red blood cells, as well as producing antibodies and storing lymphocytes.
- The lymphatic system also includes lymph nodes, tonsils, and the bone marrow, all of which play a role in the immune response and overall health of the body.
Key Terms:
- Lymphatic System Cells: Cells that play a crucial role in the function of the lymphatic system, including lymphocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells.
- Immune Function: The body’s ability to defend against pathogens and foreign substances through various mechanisms such as the production of antibodies and activation of immune cells.
- Lymphocytes: White blood cells that are key components of the immune system, including B cells, T cells, and natural killer cells.
- Macrophages: Phagocytic cells that engulf and digest pathogens, dead cells, and debris in the body.
- Dendritic Cells: Antigen-presenting cells that play a crucial role in initiating an immune response by presenting antigens to T cells.
- Antibodies: Proteins produced by B cells that recognize and neutralize specific antigens, such as viruses or bacteria.
- Antigens: Molecules that can trigger an immune response, leading to the production of antibodies and activation of immune cells.