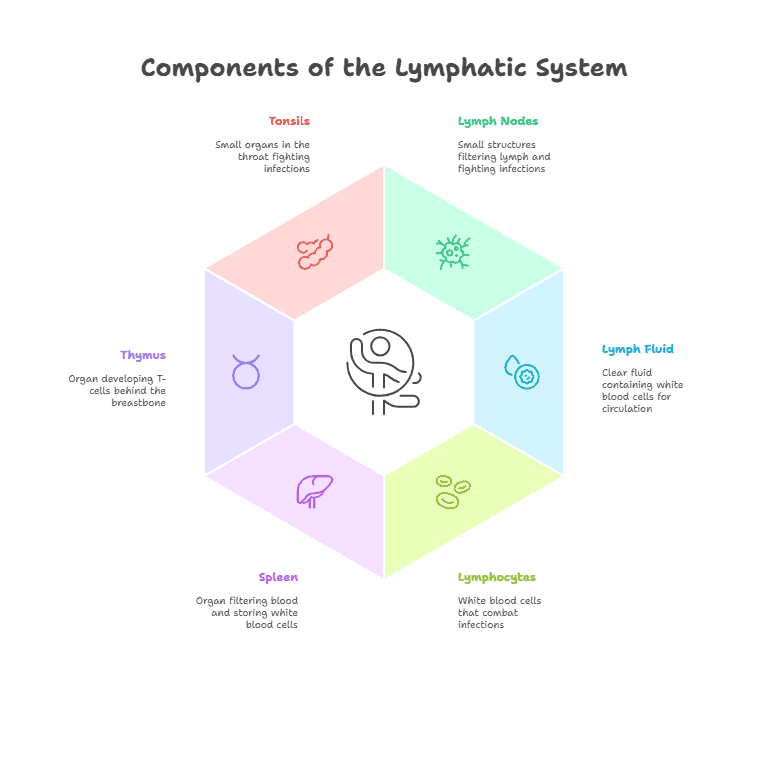
The lymphatic system is a vital part of the body’s immune system, responsible for protecting the body against infections and diseases. It is a network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials. Understanding the anatomy of the lymphatic system is crucial in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Lymphatic Vessels
The lymphatic vessels are a network of thin tubes that carry lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the body. These vessels are similar to blood vessels but have a different purpose. They help transport lymph from tissues back into the bloodstream and play a key role in the body’s immune response.
Lymph Nodes
Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures located along the lymphatic vessels. They act as filters, trapping bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances before they can reach the bloodstream. Lymph nodes also contain white blood cells, which help fight off infections and diseases.
Spleen
The spleen is the largest organ in the lymphatic system and is located in the upper left part of the abdomen. It acts as a filter for blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells and helping to fight off infections. The spleen also plays a role in producing white blood cells and storing blood platelets.
Thymus
The thymus is a small organ located behind the breastbone and plays a crucial role in the development of the immune system. It is responsible for producing and maturing T-cells, a type of white blood cell that helps fight off infections and diseases. The thymus is most active during childhood and gradually decreases in size as we age.
Tonsils and Adenoids
The tonsils and adenoids are small masses of tissue located in the back of the throat. They help trap bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth and nose, preventing them from causing infections. The tonsils and adenoids also contain white blood cells that help fight off pathogens.
Summary
In summary, the lymphatic system is a complex network of tissues and organs that play a crucial role in the body’s immune response. Understanding the anatomy of the lymphatic system, including lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, spleen, thymus, tonsils, and adenoids, is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The lymphatic system is a network of vessels and organs that help maintain fluid balance in the body.
- Lymphatic vessels carry lymph, a clear fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the body.
- Lymph nodes are small structures that filter lymph and help fight infection.
- The spleen, thymus, and tonsils are also important organs in the lymphatic system.
- The lymphatic system plays a key role in the immune system by helping to remove toxins and waste from the body.
Key Terms:
- Lymphatic System: A network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials.
- Lymph Nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph fluid and contain immune cells that help fight infection.
- Lymph Fluid: A clear fluid that contains white blood cells and drains waste from the body’s tissues.
- Spleen: An organ that filters and stores blood, and helps with the production of white blood cells.
- Thymus: An organ located in the chest that helps with the production and maturation of white blood cells.
- Tonsils: Small masses of tissue in the back of the throat that help fight infection.
- Bone Marrow: Soft tissue found in the center of bones that produces blood cells, including lymphocytes.