The lymphatic system is a vital part of the body’s immune system, responsible for protecting the body from infections and diseases. It is a network of tissues and organs that work together to remove toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials from the body and transport lymph, a fluid containing white blood cells, throughout the body.
Functions of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system has several key functions, including:
- Draining excess fluid from tissues
- Transporting fats from the digestive system
- Producing and storing white blood cells
- Filtering and removing waste and toxins
Components of the Lymphatic System
The lymphatic system comprises lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, the thymus, the spleen, and the tonsils. Lymphatic vessels are similar to blood vessels and carry lymph throughout the body. Lymph nodes are small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph and trap bacteria and viruses. The thymus is responsible for producing T-cells, a type of white blood cell, while the spleen filters blood and helps fight infections. The tonsils are located in the back of the throat and help prevent infections.
Role in Immune Function
The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in immune function by producing and storing white blood cells, which help the body fight off infections. Lymph nodes act as checkpoints for the immune system, filtering out harmful substances and producing antibodies to fight off infections. Without a properly functioning lymphatic system, the body would be more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Common Lymphatic System Disorders
Disorders of the lymphatic system can lead to a variety of health problems, including lymphedema, which is swelling caused by a blockage in the lymphatic vessels. Other disorders include lymphoma, a type of cancer that affects the lymphatic system, and tonsillitis, an infection of the tonsils. It is important to maintain a healthy lymphatic system through proper diet, exercise, and regular medical check-ups.
Summary
In summary, the lymphatic system is a complex network of tissues and organs that play a crucial role in immune function. It helps remove waste and toxins from the body, transports lymph throughout the body, and produces white blood cells to fight off infections. Disorders of the lymphatic system can lead to serious health problems, so it is important to maintain a healthy lymphatic system through proper care and attention.
Key Takeaways:
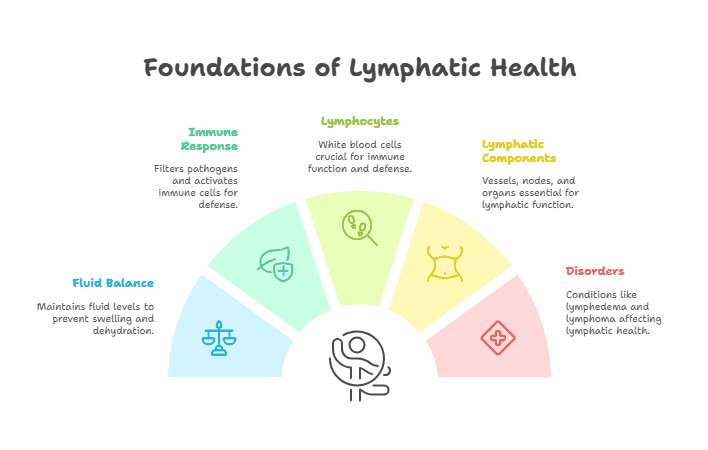
- The lymphatic system plays a crucial role in maintaining fluid balance in the body.
- Lymphatic vessels, lymph nodes, and lymphoid organs are key components of the lymphatic system.
- The lymphatic system helps in immune response by filtering and trapping pathogens and foreign particles.
- Lymphocytes, a type of white blood cell, are essential for the immune function of the lymphatic system.
- Disorders of the lymphatic system can lead to conditions such as lymphedema and lymphoma.
Key Terms:
- Lymphatic System: A network of tissues and organs that help rid the body of toxins, waste, and other unwanted materials.
- Lymph Nodes: Small, bean-shaped structures that filter lymph fluid and help fight infection.
- Lymph Fluid: A clear fluid that contains white blood cells and circulates throughout the lymphatic system.
- Lymphocytes: A type of white blood cell that helps the body fight off infections and diseases.
- Spleen: An organ that filters blood and stores white blood cells.
- Thymus: An organ located behind the breastbone that helps develop T-cells, a type of white blood cell.
- Tonsils: Small organs located in the back of the throat that help fight off infections.