The cardiovascular system is a complex network of organs and tissues that work together to transport oxygen, nutrients, and waste products throughout the body. One of the key components of this system is the blood vessels, which play a crucial role in maintaining the health and function of the circulatory system.
1. Transport of Blood
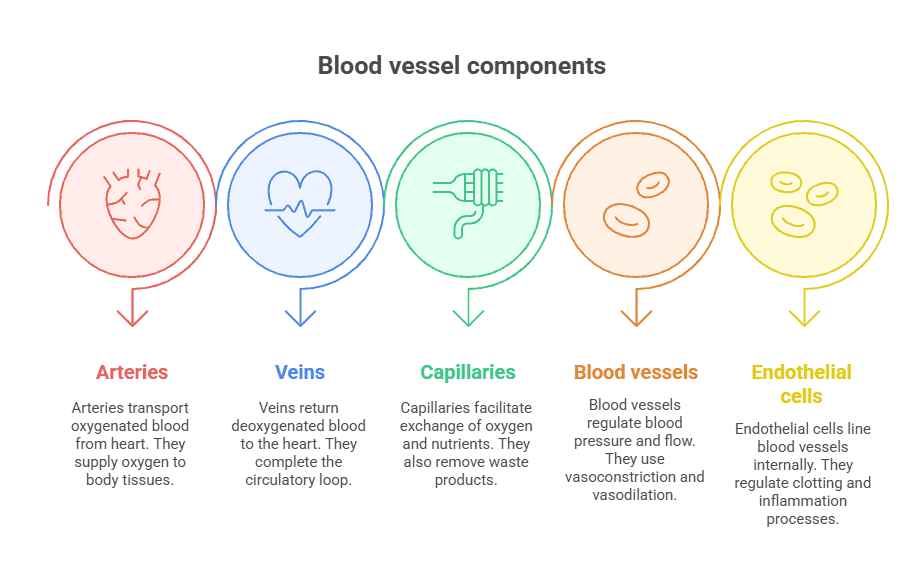
One of the primary functions of blood vessels is to transport blood throughout the body. Arteries carry oxygen-rich blood away from the heart to the tissues, while veins bring oxygen-poor blood back to the heart. Capillaries, the smallest blood vessels, facilitate the exchange of nutrients and waste products between the blood and the surrounding tissues.
2. Regulation of Blood Pressure
Blood vessels play a key role in regulating blood pressure. Arteries have the ability to constrict or dilate in response to various stimuli, such as changes in blood volume or levels of certain hormones. This helps to maintain a constant blood pressure and ensure adequate blood flow to all parts of the body.
3. Thermoregulation
Blood vessels also play a role in thermoregulation, or the regulation of body temperature. When the body becomes too hot, blood vessels near the skin surface dilate, allowing more blood to flow to the skin where heat can be released. Conversely, when the body is cold, blood vessels constrict to reduce blood flow to the skin and conserve heat.
4. Immune Response
Blood vessels are also involved in the body’s immune response. When tissues are damaged or infected, white blood cells and other immune cells are transported to the site of injury or infection via the bloodstream. Blood vessels help to facilitate this process by allowing these cells to leave the bloodstream and enter the affected tissues.
Summary
In summary, blood vessels play a crucial role in the cardiovascular system by transporting blood, regulating blood pressure, facilitating thermoregulation, and supporting the body’s immune response. Understanding the functions of blood vessels is essential for maintaining overall cardiovascular health and ensuring proper functioning of the circulatory system.
Key Takeaways:
- Arteries carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the body’s tissues
- Veins carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart
- Capillaries are tiny blood vessels where oxygen and nutrients are exchanged for waste products
- Blood vessels help regulate blood pressure and flow through vasoconstriction and vasodilation
- Endothelial cells line the inside of blood vessels and help regulate blood clotting and inflammation
Key Terms:
- Blood vessels: Tubular structures that carry blood throughout the body.
- Arteries: Blood vessels that carry oxygenated blood away from the heart to the rest of the body.
- Veins: Blood vessels that carry deoxygenated blood back to the heart.
- Capillaries: Tiny blood vessels where gas exchange and nutrient exchange occurs between the blood and tissues.
- Vasoconstriction: The narrowing of blood vessels, which causes an increase in blood pressure.
- Vasodilation: The widening of blood vessels, which causes a decrease in blood pressure.
- Endothelium: The inner lining of blood vessels that helps regulate blood flow and vessel tone.
- Peripheral resistance: The resistance to blood flow in the arteries, which affects blood pressure.