Welcome to the learning module on the Skeletal System! In this module, we will examine the bones that comprise our body and how they work together to support and protect us. By the end of this module, you will have a better understanding of the various types of bones in the human body and their functions.
Objectives:
- Identify the different types of bones in the human body
- Understand the functions of the skeletal system
- Learn how bones grow and change over time
- Explore common injuries and diseases of the skeletal system
Section 1: What is the Skeletal System?
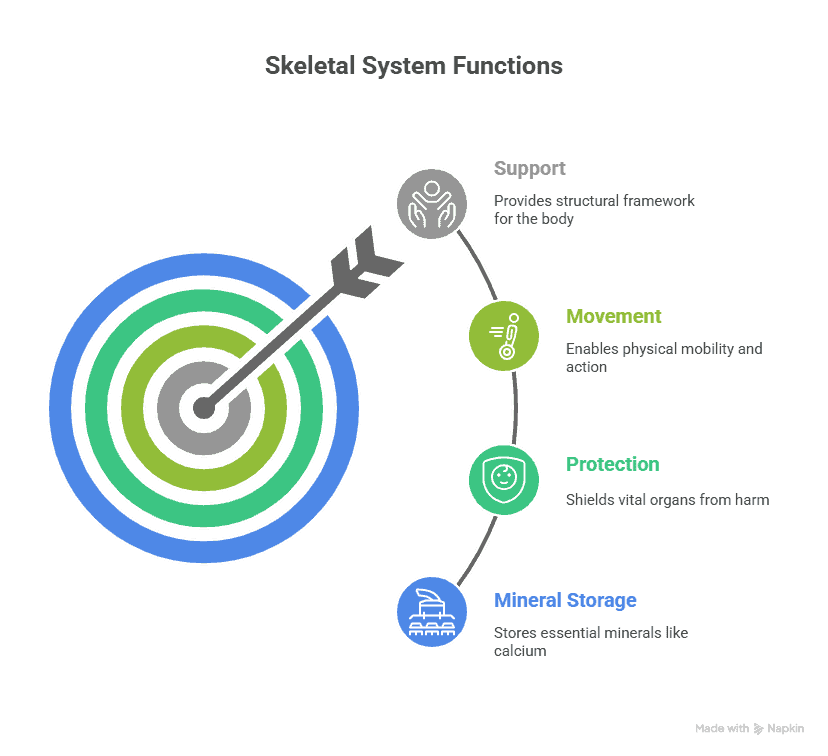
The skeletal system is the framework of bones that supports the human body. It helps us move, stand up straight, and protect our organs. Our bones also store minerals like calcium and phosphorus. There are 206 bones in the adult human body, ranging in size from tiny bones in our ears to large bones like the femur in our legs. Without our skeletal system, we would be like a blob with no shape or structure!
Structure of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system consists of bones, joints, and cartilage. Bones are hard and provide structure and support to the body. Joints are where two bones meet, allowing for the movement of the bones. Cartilage is a smooth, rubbery tissue that cushions joints and helps them move smoothly. Together, these components work to help us move, stand, and protect our organs.
Functions of the Skeletal System
The skeletal system has several essential functions. It provides support for our bodies, helping us stand up straight and move around. It protects our internal organs, such as the heart and lungs, from injury. The bones also store essential minerals, such as calcium, that our bodies need to remain healthy. Additionally, the skeletal system works in conjunction with muscles to enable us to move and perform activities such as running, jumping, and dancing.
Games and Activities
Here are some games and activities to help reinforce your knowledge of the skeletal system
Section 2: Types of Bones
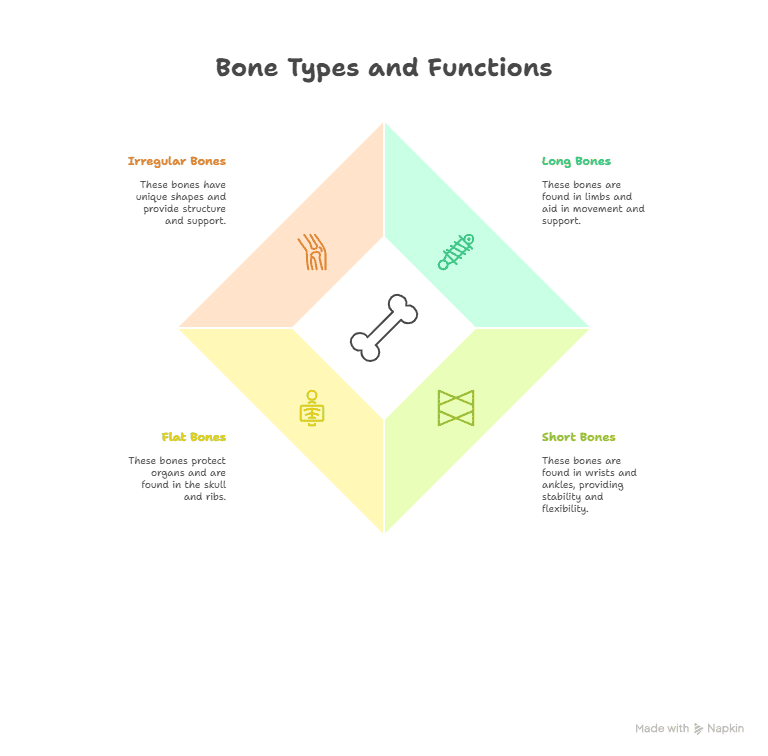
In the human body, there are different types of bones. Long bones, such as those in our arms and legs, help us move and support our bodies. Short bones, such as those in our wrists and ankles, contribute to stability and flexibility. Flat bones, such as the ones in our skull and ribs, protect our organs. Irregular bones, such as those in our spine and hips, have unique shapes that provide structure and support. Each type of bone plays a crucial role in maintaining our strength and overall health.
Bone Type List
| Bone Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Long bones | Bones that are longer than they are wide, such as the femur and humerus. |
| Short bones | Bones that are approximately equal in length and width, such as the carpals in the wrist. |
| Flat bones | Bones that are thin, flat, and curved, such as the ribs and skull bones. |
| Irregular bones | Bones that do not fit into the other categories, such as the vertebrae and facial bones. |
| Sesamoid bones | Small, round bones embedded in tendons, such as the patella (kneecap). |
Bone Anatomy
Bone anatomy is the study of the structure and function of bones in the human body. Bones are hard, strong parts of our body that give us shape and support. They protect our organs and help us move. Bones are made up of minerals like calcium and phosphorus.
Inside bones, there is bone marrow where blood cells are made. Bones come in different shapes and sizes, like long bones in our arms and legs, and flat bones in our skull. Taking care of our bones by eating a healthy diet and engaging in regular exercise is essential for maintaining strength and overall health.
Bone Structure
Bone structure refers to the arrangement of bones within the body. Bones are like the framework that holds our body upright and gives it shape.
They are made up of hard tissue that protects our organs and helps us move. The structure of bones consists of an outer layer called the periosteum, compact bone in the middle, and spongy bone within. Joints are where bones come together, allowing us to bend and move.
Taking care of our bone structure is crucial for maintaining good health and overall strength.
Bone Cells
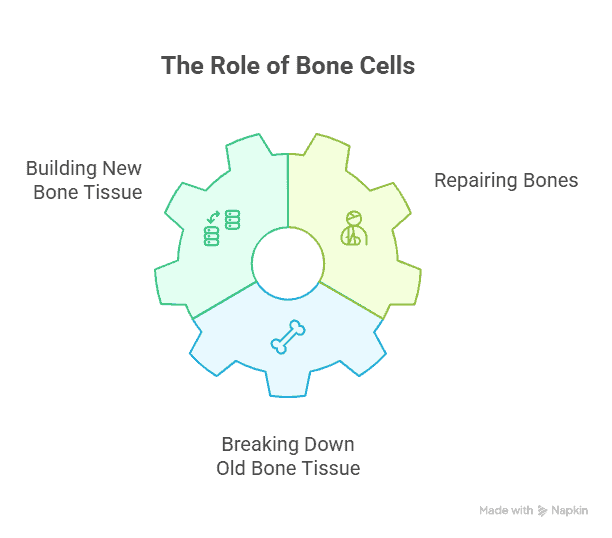
Bone cells are small cells that comprise the bones in the human body. They help to build and repair bones, keeping them strong and healthy. There are different types of bone cells, each with its essential job. Some bone cells help to break down old bone tissue, while others help to build new bone tissue. Together, these bone cells work to keep our bones strong and support our bodies.
Types of Bone Cells
| Type of Bone Cell | Definition |
|---|---|
| Osteoblasts | These are cells responsible for building new bone tissue. They produce proteins and minerals that form the matrix of bone. |
| Osteoclasts | These cells break down bone tissue by releasing enzymes that dissolve the minerals in bone, helping to regulate calcium levels in the body. |
| Osteocytes | These are mature bone cells that maintain bone tissue by sensing and responding to changes in mechanical stress on the bone. |
| Osteoprogenitor Cells | These cells are bone stem cells that can differentiate into osteoblasts, helping in the repair and regeneration of bone tissue. |
Bone Growth and Remodeling
Bone growth and remodeling are crucial processes that help maintain the strength and health of our bones. When we are young, our bones grow and get longer as we grow taller. This is called bone growth. As we age, our bones require constant repair and rebuilding to remain strong.
This is called bone remodeling. Our bones are composed of living tissue that constantly changes and adapts to meet our body’s needs. By eating healthy foods, engaging in regular exercise, and taking care of our bodies, we can help maintain strong bones and prevent conditions like osteoporosis later in life.
Games and Activities
Use these games and activities to help you learn and retain information about bone structures and cells.
Bone Types
Bone Cells
Section 3: Joint Types and Movements
Joints are places where two bones meet. The human body has various types of joints. Some joints, such as the shoulder and hip joints, can move in multiple directions.
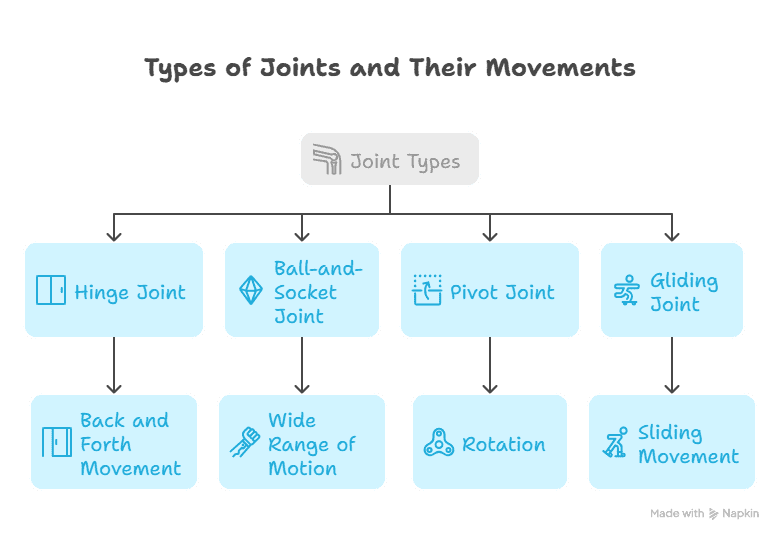
Types of Joints
The human body has various types of joints. The most common type is called a hinge joint, which allows our bones to move back and forth like a door hinge. Another type is a ball-and-socket joint, where one bone has a rounded end that fits into a cup-like socket of another bone.
There are also pivot joints, which allow bones to rotate around each other, and gliding joints, which let bones slide past each other. Each type of joint has its unique role in helping us move and remain flexible.
List of Joint Types
| Joint Type | Definition |
|---|---|
| Ball and Socket Joint | A joint that allows for the widest range of motion, with the rounded end of one bone fitting into a cup-like socket of another bone. |
| Hinge Joint | A joint that allows for movement in only one plane, like a door hinge. |
| Pivot Joint | A joint that allows for rotational movement around a central axis. |
| Gliding Joint | A joint that allows for sliding or twisting movements between bones. |
| Condyloid Joint | A joint that allows for movement in two planes, like the wrist joint. |
| Saddle Joint | A joint that allows for movement in two planes, similar to a condyloid joint but with greater range of motion. |
| Synchondrosis Joint | A joint where bones are joined by hyaline cartilage, allowing for slight movement. |
| Syndesmosis Joint | A joint where bones are connected by ligaments, allowing for limited movement. |
| Cartilaginous Joint | A joint where bones are connected by fibrocartilage or hyaline cartilage, allowing for slight movement. |
| Synovial Joint | A joint with a fluid-filled cavity that allows for a wide range of motion. |
Joint Movements
Joint movements refer to the way our bones move within our bodies. Various types of joint movements enable us to perform everyday tasks such as walking, jumping, and bending.
Some joints can only move in one direction, like our knees when we bend them. Other joints, such as our shoulders, can move in multiple directions. Our joints are essential for helping us move and be active every day.
| Joint Movement | Definition |
|---|---|
| Flexion | Decreasing the angle between two bones |
| Extension | Increasing the angle between two bones |
| Abduction | Moving a body part away from the midline of the body |
| Adduction | Moving a body part towards the midline of the body |
| Rotation | Turning a body part around its axis |
| Circumduction | Moving a body part in a circular motion |
| Dorsiflexion | Flexing the foot upwards towards the shin |
| Plantarflexion | Pointing the foot downwards away from the shin |
| Pronation | Rotating the forearm so that the palm faces downwards |
| Supination | Rotating the forearm so that the palm faces upwards |
Common Joint Injuries
Joint injuries are common among individuals who participate in sports or engage in physical activity. They can happen when you twist, fall, or overuse a joint. Some common joint injuries include sprains, strains, and dislocations.
A sprain occurs when the ligaments surrounding a joint become stretched or torn. A strain occurs when the muscles or tendons surrounding a joint become injured. A dislocation occurs when a bone in a joint is forced out of its normal position. It’s essential to rest, ice, compress, and elevate an injured joint. If the pain persists, it’s a good idea to consult a doctor for assistance.
Games and Activities
Use these games and activities to boost your understanding of the joints and their functions.
Joints
Movements
Conclusion
You’ve completed the learning module on the Skeletal System! Throughout this module, you have learned about the following objectives:
- The functions of the skeletal system
- The different types of bones in the body
- How bones grow and develop
- Common skeletal system disorders
By understanding these key concepts, you now have a deeper appreciation for the importance of caring for your skeletal system. Remember to eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly, and practice good posture to keep your bones strong and healthy. Great job on completing this module!
What to Study Next?
Great job on studying the skeletal system! Now, it’s a good idea to learn about the muscular system next. The muscular system is responsible for helping your body move and maintain its strength. By understanding how your muscles function, you can learn how to maintain their health and stability.
You can start by learning about the different types of muscles in your body and how they work together. This will help you understand the importance of exercising and taking care of your muscles. Keep up the good work!