Welcome to our learning module on the Endocrine System! In this module, we will examine the crucial role that the endocrine system plays in regulating various bodily functions. The endocrine system comprises glands that produce hormones, which act as messengers to regulate processes such as growth, metabolism, and mood. Understanding how the endocrine system works is crucial for comprehending how our bodies function.
Objectives:
- Discover the various glands that comprise the endocrine system.
- Understand the functions of hormones in the body.
- Discover how the endocrine system regulates metabolism, growth, and other bodily functions.
- Identify common endocrine disorders and their symptoms.
- Discuss how lifestyle choices can impact the health of the endocrine system.
Section 1: What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a group of glands in our body that produce hormones. Hormones are chemical messengers that travel through our bloodstream and help regulate critical bodily functions.
These functions include regulating metabolism, growth, sleep, mood, and reproduction. The endocrine system works in conjunction with the nervous system to maintain our body’s balance and proper functioning.
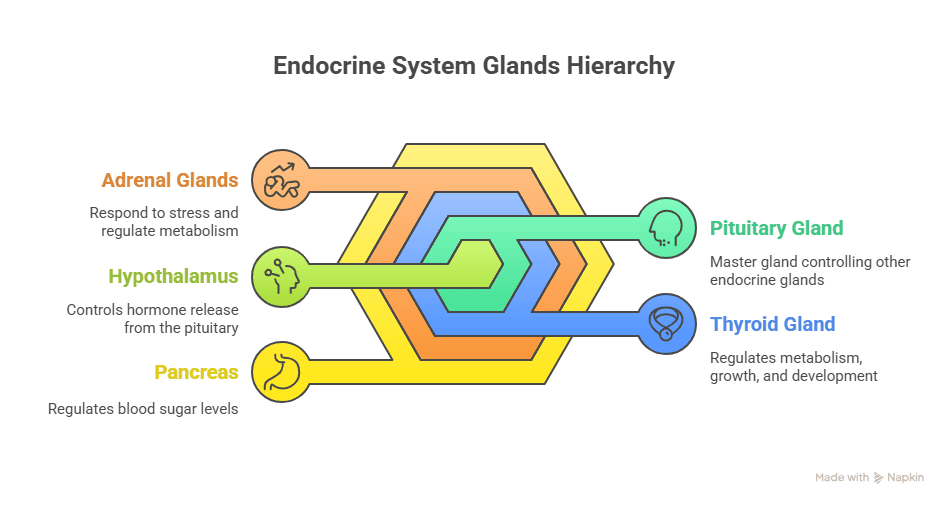
| Endocrine System | Definition |
|---|---|
| Hypothalamus | A small region of the brain that controls the release of hormones from the pituitary gland. |
| Pituitary Gland | The “master gland” that controls the activity of other endocrine glands in the body. |
| Thyroid Gland | Produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development. |
| Adrenal Glands | Produce hormones that help the body respond to stress and regulate metabolism. |
| Pancreas | Produces insulin and glucagon, which regulate blood sugar levels. |
| Ovaries | Produce estrogen and progesterone, which regulate the menstrual cycle and fertility. |
| Testes | Produce testosterone, which regulates sperm production and male characteristics. |
Endocrine Glands
The human body has several major endocrine glands that help regulate key bodily functions. The pituitary gland, often referred to as the “master gland,” regulates other glands and produces hormones that influence growth, reproduction, and metabolism.
The thyroid gland produces hormones that regulate metabolism and energy levels. The adrenal glands produce hormones that help the body respond to stress and regulate blood pressure.
The pancreas produces insulin, which helps regulate blood sugar levels. The ovaries and testes produce hormones that regulate sexual development and reproduction. These glands work together to maintain the proper functioning of our bodies.
Games and Activities
- Endocrine System Flashcards
- Endocrine Quiz
- Endocrine Glands Flashcards
- Endocrine Glands Quiz
- Endocrine System Vocabulary Hangman
- Endocrine Glands Vocabulary Hangman
Section 2: Hormones
Hormones are chemicals in our body that act as messengers, telling different parts of our body what to do. They are made in various glands and travel through our bloodstream to reach their target organs.
These hormones help regulate essential bodily functions, including growth, metabolism, mood, and reproduction. For example, the hormone insulin helps control our blood sugar levels, while adrenaline helps us respond to stress.
When our hormones are balanced and working correctly, our body functions smoothly. However, if there is an imbalance in our hormones, it can lead to health problems.
List of Endocrine Hormones
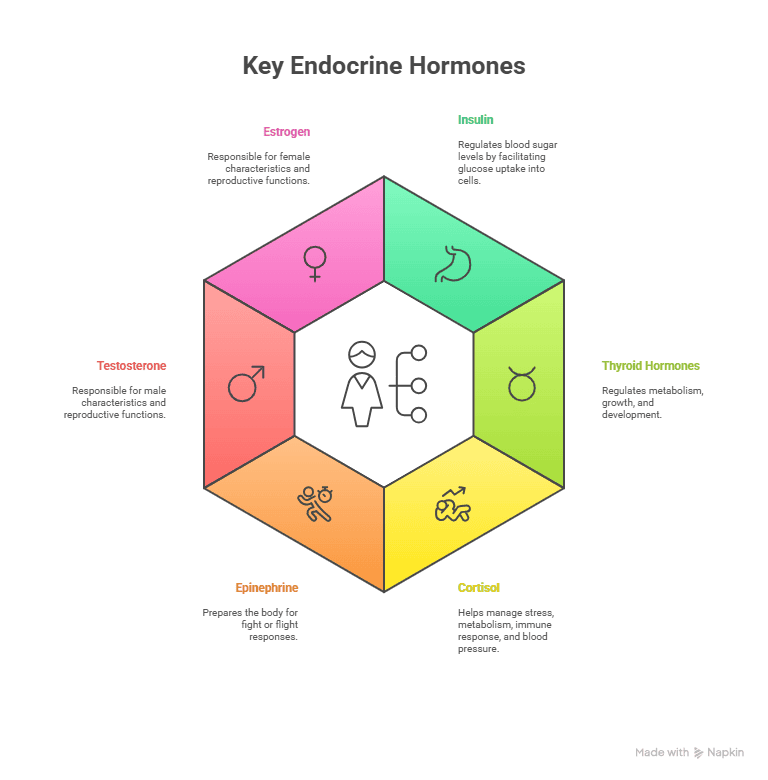
| Endocrine Hormone | Definition |
|---|---|
| Insulin | A hormone produced by the pancreas that regulates blood sugar levels by allowing cells to take in glucose for energy. |
| Thyroid Hormones (T3 and T4) | Hormones produced by the thyroid gland that regulate metabolism, growth, and development. |
| Cortisol | A stress hormone produced by the adrenal glands that helps regulate metabolism, immune response, and blood pressure. |
| Epinephrine (Adrenaline) | A hormone produced by the adrenal glands that prepares the body for fight or flight response in stressful situations. |
| Testosterone | A hormone produced by the testes in males and in small amounts by the adrenal glands in both males and females, responsible for male characteristics and reproductive functions. |
| Estrogen | A hormone produced by the ovaries in females and in small amounts by the adrenal glands in both males and females, responsible for female characteristics and reproductive functions. |
Section 3: Hormone Regulation
Feedback Mechanisms
Hormones in the body are regulated through a series of feedback mechanisms. This means that the body uses signals to control the levels of hormones in the blood. When hormone levels get too high, the body sends a signal to decrease production.
When levels are too low, the body sends a signal to increase production. This helps maintain balance in the body and ensures that hormones are at the proper levels to keep the body functioning correctly.
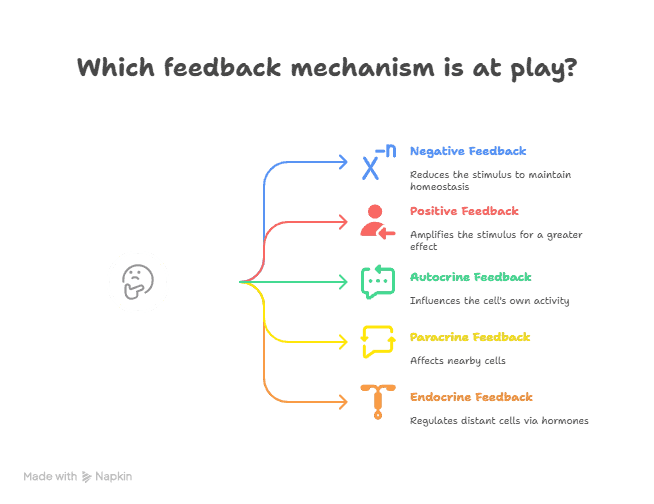
| Feedback Mechanism | Definition |
|---|---|
| Negative Feedback | A regulatory mechanism in which a stimulus initiates a response that reduces the stimulus, maintaining homeostasis. |
| Positive Feedback | A regulatory mechanism in which a stimulus initiates a response that increases the stimulus, often leading to an amplified effect. |
| Autocrine Feedback | A feedback mechanism in which a cell secretes a signaling molecule that binds to receptors on its own surface, influencing its own activity. |
| Paracrine Feedback | A feedback mechanism in which a cell secretes a signaling molecule that acts on nearby cells, influencing their activity. |
| Endocrine Feedback | A feedback mechanism in which hormones are released into the bloodstream to regulate the activity of distant target cells or organs. |
Hormone Action
At the cellular level, hormones bind to specific receptors on the surface of target cells. These receptors act like a lock and key, only allowing the hormone to fit into them.
Once the hormone binds to the receptor, it triggers a series of events within the cell. This can include activating enzymes, changing gene expression, or altering cell membrane permeability.
These actions ultimately lead to a specific response in the cell, such as protein synthesis, cell growth, or metabolism. Hormones can have different effects on various types of cells, depending on the receptors they bind to and the signaling pathways they activate.
Endocrine Disorders
Endocrine disorders are conditions that affect the body’s hormones. Some common endocrine disorders include diabetes, thyroid disorders, and adrenal gland disorders. These disorders can have a significant impact on a person’s health.
For example, diabetes can lead to high blood sugar levels, which can cause damage to organs like the kidneys and eyes. Thyroid disorders can affect metabolism and energy levels, while adrenal gland disorders can cause issues with stress response and blood pressure.
Pre-med students need to understand these disorders so they can help patients manage their symptoms and improve their overall health.
| Endocrine Disorder | Definition |
|---|---|
| Diabetes | A disorder in which the body is unable to properly regulate blood sugar levels, leading to high blood sugar levels (hyperglycemia). |
| Hypothyroidism | A condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough thyroid hormones, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight gain, and cold intolerance. |
| Hyperthyroidism | A condition in which the thyroid gland produces too much thyroid hormone, leading to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and heat intolerance. |
| Addison’s disease | A rare disorder in which the adrenal glands do not produce enough cortisol and aldosterone, leading to symptoms such as fatigue, weight loss, and low blood pressure. |
| Cushing’s syndrome | A condition in which the body is exposed to high levels of cortisol for a prolonged period of time, leading to symptoms such as weight gain, muscle weakness, and high blood pressure. |
Games and Activities
Section 4: Endocrine System in Health and Disease
Endocrine System and Homeostasis
The endocrine system helps maintain our body’s balance, or homeostasis. It does this by releasing hormones into the bloodstream, which then travel to different parts of the body to regulate processes such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
For example, if the body is too hot, the endocrine system releases hormones that tell the body to sweat to cool down. If the body is too cold, the endocrine system releases hormones that tell the body to shiver to generate heat.
Endocrine System and Reproduction
The endocrine system plays a vital role in reproductive functions. It is responsible for producing hormones that regulate the menstrual cycle in females and sperm production in males.
These hormones help control when and how the body releases eggs, prepare the uterus for pregnancy, and influence the development of secondary sexual characteristics.
Without the endocrine system, our bodies would not be able to regulate the reproductive process properly. It is essential for maintaining a healthy reproductive system.
Endocrine System and Stress Response
When we feel stressed, our endocrine system responds. The pituitary gland releases hormones that tell the adrenal glands to produce cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones help our body respond to stress by increasing heart rate, blood pressure, and energy levels.
However, chronic stress can lead to hormonal imbalances, which can impact our overall health. It can weaken our immune system, disrupt our sleep, and even contribute to conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes.
It’s essential to manage stress through activities such as exercise, relaxation techniques, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle to keep our endocrine system in balance and support our overall well-being.
Conclusion
You’ve completed the learning module on the Endocrine System! Congrats on finishing the course. Here are the objectives you’ve learned:
- Understand the function of the endocrine system
- Identify the major endocrine glands in the body
- Learn about the hormones produced by each gland
- Understand how hormones regulate bodily functions
- Recognize common endocrine disorders
Keep up the great work in learning about anatomy! Remember to review the material regularly to solidify your understanding. Happy studying!
What to Study Next?
Great job studying the Endocrine system! Now, I suggest you move on to learning the Reproductive system next. This system is crucial for understanding how babies are formed and how our bodies change as we age.
It’s fascinating to learn about how the male and female reproductive organs work together to create new life. By studying the Reproductive system, you’ll gain a better understanding of how our bodies are designed to continue the human race. Keep up the good work!