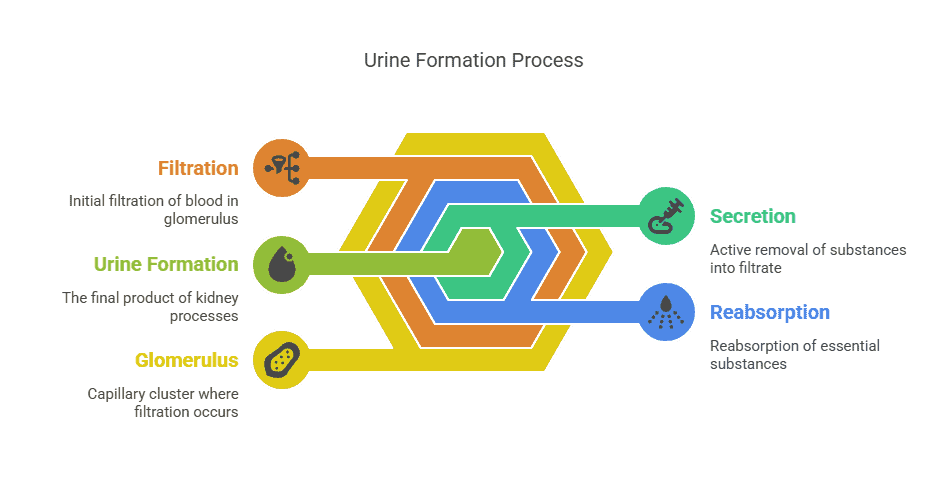
The process of urine formation and filtration is a crucial function of the urinary system. The kidneys play a vital role in filtering waste products from the blood and regulating the body’s fluid balance. This process involves several complex steps that ultimately result in the formation of urine, which is then excreted from the body.
Filtration
The first step in urine formation is filtration, which takes place in the glomerulus, a cluster of blood capillaries located in the renal corpuscle of the kidney. As blood flows through the glomerulus, small molecules such as water, ions, and waste products are filtered out of the blood and into the renal tubule. This initial filtration process is essential for removing waste products and excess substances from the blood.
Reabsorption
After filtration, the filtrate moves through the renal tubule, where the process of reabsorption occurs. In this step, essential substances such as water, glucose, and ions are reabsorbed back into the blood to maintain the body’s balance of electrolytes and fluids. The reabsorption process helps to conserve valuable nutrients and maintain the body’s overall homeostasis.
Secretion
Once reabsorption is complete, the remaining filtrate continues through the renal tubule, where the process of secretion occurs. In this step, additional waste products and excess substances are actively transported from the blood into the filtrate to be excreted from the body. Secretion helps to further eliminate harmful substances and maintain the body’s internal environment.
Summary
Overall, the process of urine formation and filtration is a complex and essential function of the urinary system. Filtration in the glomerulus removes waste products from the blood, reabsorption conserves essential substances, and secretion eliminates additional waste products. Together, these processes help to maintain the body’s fluid balance, regulate electrolyte levels, and remove harmful substances from the body through the excretion of urine.
Key Takeaways:
- The process of urine formation involves filtration, reabsorption, secretion, and excretion.
- Filtration occurs in the glomerulus, where blood is filtered to form urine.
- Reabsorption takes place in the renal tubules, where essential substances are reabsorbed back into the bloodstream.
- Secretion involves the movement of waste products from the blood into the urine.
- Excretion is the final step where urine is eliminated from the body through the urethra.
- The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining the body’s overall fluid balance and eliminating waste products.
- Disruption in the urine formation process can lead to various health issues such as kidney stones, urinary tract infections, and kidney disease.
Key Terms:
- Urine Formation: The process by which the kidneys filter waste products and excess substances from the blood to produce urine.
- Filtration: The process by which blood is filtered in the glomerulus of the kidney to remove waste products and excess substances.
- Glomerulus: A cluster of capillaries in the kidney where filtration of blood takes place.
- Nephron: The functional unit of the kidney responsible for urine formation.
- Reabsorption: The process by which the kidneys reabsorb essential substances, such as water and electrolytes, back into the blood from the filtrate.
- Secretion: The process by which the kidneys actively remove substances, such as drugs and toxins, from the blood into the filtrate.
- Renal Tubules: The structures in the kidney where reabsorption and secretion take place to form urine.