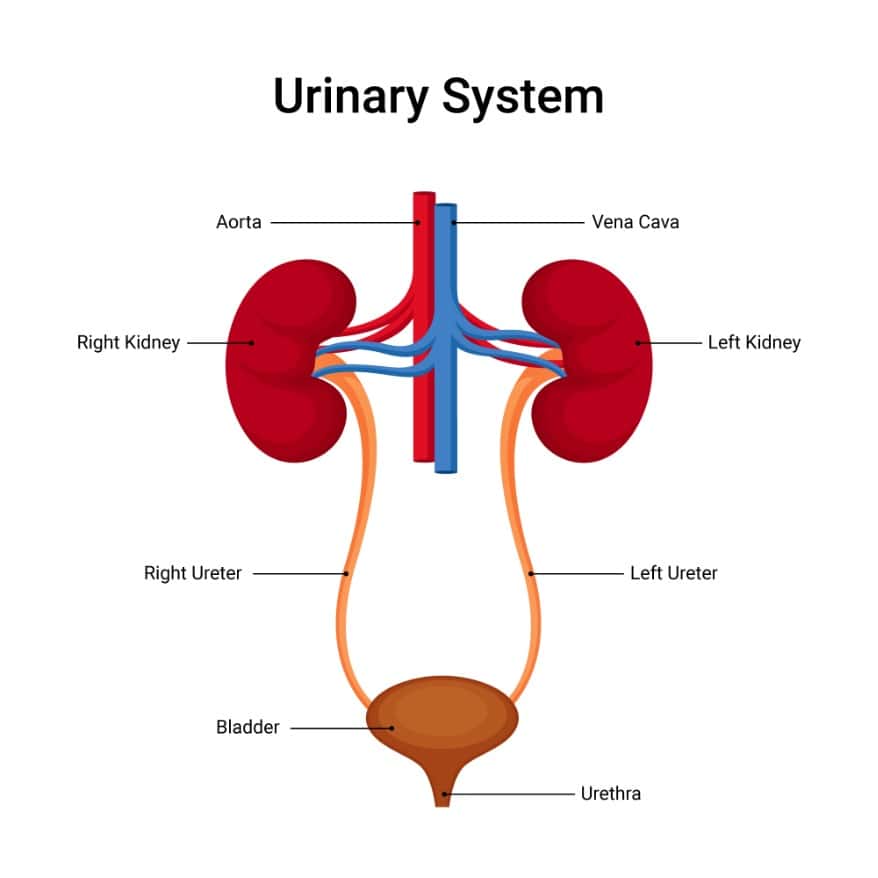
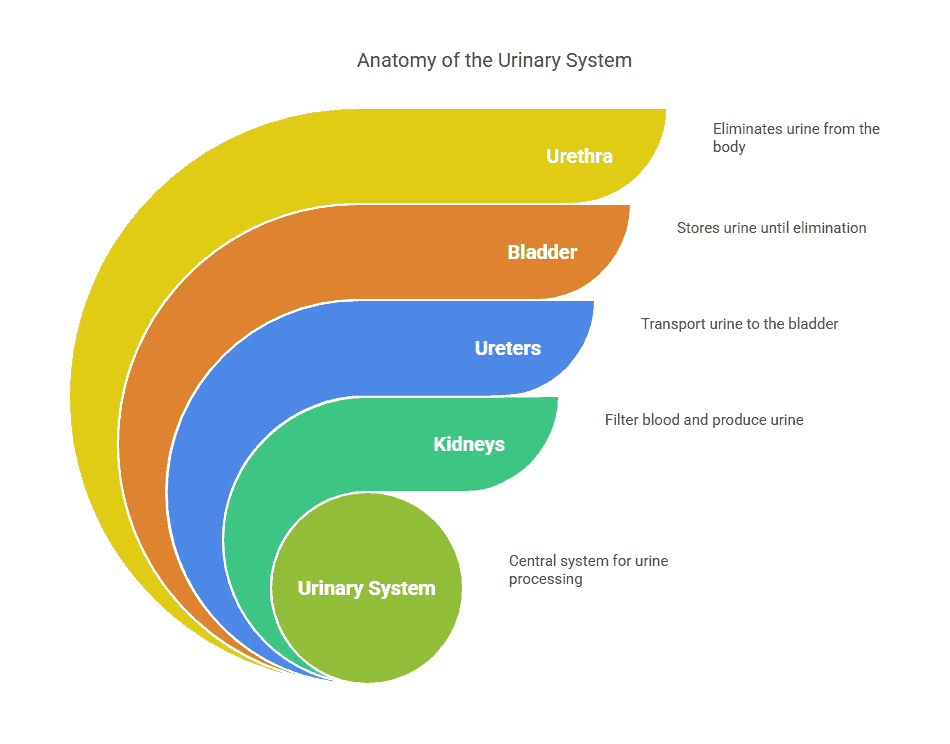
The urinary system is responsible for filtering and removing waste products from the blood to form urine, which is then excreted from the body. It consists of several organs that work together to maintain the body’s fluid balance and eliminate waste. Understanding the anatomy of the urinary system is essential for understanding how it functions and how to keep it healthy.
Organs of the Urinary System
The main organs of the urinary system include the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are bean-shaped organs located on either side of the spine, just below the rib cage. They filter waste products and excess fluids from the blood to produce urine. The urine then travels through the ureters, which are tubes that connect the kidneys to the bladder. The bladder stores urine until it is ready to be excreted through the urethra, a tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
Functions of the Urinary System
The primary function of the urinary system is to maintain the body’s fluid balance by regulating the volume and composition of the blood. The kidneys filter waste products, excess salts, and water from the blood to produce urine. They also help regulate blood pressure, produce hormones that control red blood cell production, and maintain the body’s acid-base balance.
Common Urinary System Disorders
There are several disorders that can affect the urinary system, including urinary tract infections, kidney stones, and kidney disease. Urinary tract infections occur when bacteria enter the urinary tract and multiply, causing symptoms such as pain, burning during urination, and frequent urination. Kidney stones are hard deposits of minerals and salts that form in the kidneys and can cause severe pain when they pass through the urinary tract. Kidney disease can result from a variety of factors, including diabetes, high blood pressure, and genetic disorders, and can lead to kidney failure if left untreated.
Summary
In summary, the urinary system is a complex system of organs that work together to filter waste products from the blood and produce urine. The kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra all play a role in maintaining the body’s fluid balance and eliminating waste. Understanding the anatomy of the urinary system is crucial for maintaining overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
- The kidneys filter blood to remove waste products and excess fluids, producing urine
- The ureters are tubes that transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder
- The bladder stores urine until it is expelled from the body through the urethra
- The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance in the body
- Damage or dysfunction of the urinary system can lead to various health problems
Key Terms:
- Urinary System: The system in the body that is responsible for producing, storing, and eliminating urine.
- Kidneys: Organs in the urinary system that filter waste products from the blood to produce urine.
- Ureters: Tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder.
- Bladder: Organ that stores urine until it is ready to be eliminated from the body.
- Urethra: Tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body.
- Nephrons: Functional units of the kidneys responsible for filtering blood and producing urine.
- Renal Cortex: Outer region of the kidney where blood is filtered.
- Renal Medulla: Inner region of the kidney where urine is collected and transported to the renal pelvis.
- Renal Pelvis: Funnel-shaped structure in the kidney where urine is collected before entering the ureters.