One of the critical roles of the endocrine system is to control growth and development in the body. This regulation is essential for maintaining proper functioning and health throughout life.
How Does the Endocrine System Regulate Growth and Development?
The endocrine system works in coordination with the nervous system to regulate growth and development. Hormones are chemical messengers that are produced by the endocrine glands and are released into the bloodstream. These hormones then travel to target organs and tissues, where they trigger specific responses that help regulate growth and development.
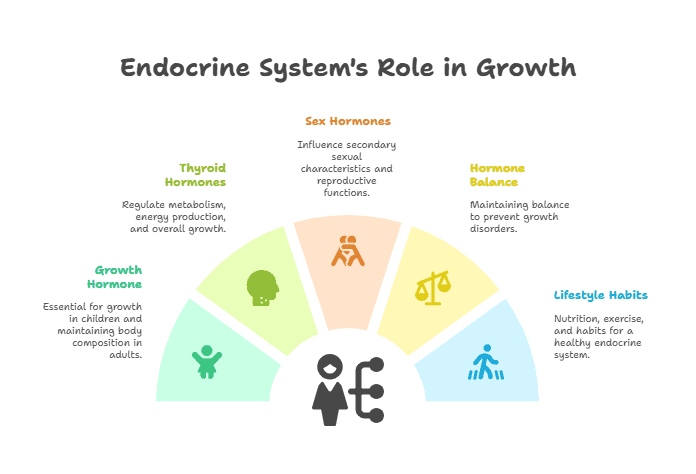
One of the key hormones involved in growth and development is growth hormone, produced by the pituitary gland. Growth hormone plays a crucial role in stimulating growth in children and adolescents, as well as regulating metabolism and body composition in adults. Other hormones, such as thyroid hormones, insulin, and sex hormones, also play important roles in growth and development.
Role of Hormones in Growth and Development
Growth hormone is essential for promoting the growth of bones and tissues, especially during childhood and adolescence. It stimulates the production of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), which is necessary for cell growth and division. Thyroid hormones, produced by the thyroid gland, are crucial for regulating metabolism and promoting growth and development.
Sex hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, play a significant role in the development of secondary sexual characteristics during puberty. These hormones also influence growth and development in other ways, such as bone density and muscle mass.
Disruption of Growth and Development
Disruptions in the endocrine system can lead to growth disorders and developmental abnormalities. For example, a deficiency in growth hormone can result in stunted growth and short stature. Thyroid disorders can also impact growth and development, leading to conditions such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism.
Imbalances in sex hormones can cause delays in puberty or abnormal development of secondary sexual characteristics. These disruptions can have long-term effects on overall health and well-being.
Summary
The endocrine system plays a vital role in regulating growth and development in the body. Hormones produced by the endocrine glands control various processes, such as bone growth, metabolism, and sexual development. Disruptions in the endocrine system can lead to growth disorders and developmental abnormalities, highlighting the importance of maintaining hormonal balance for overall health and well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The endocrine system plays a crucial role in regulating growth and development throughout the lifespan.
- Hormones released by endocrine glands control various processes, such as cell growth, differentiation, and metabolism.
- Growth hormone (GH) is essential for stimulating growth in children and maintaining healthy body composition in adults.
- Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism, energy production, and overall growth and development.
- Sex hormones, such as estrogen and testosterone, play a significant role in the development of secondary sexual characteristics and reproductive functions.
- Imbalances in hormone levels can lead to growth disorders, such as gigantism, dwarfism, and precocious puberty.
- Proper nutrition, exercise, and lifestyle habits are essential for maintaining a healthy endocrine system and promoting optimal growth and development.
Key Terms:
- Growth Hormone (GH): A hormone produced by the pituitary gland that stimulates growth and cell reproduction.
- Thyroid Hormones: Hormones produced by the thyroid gland that regulate metabolism and growth.
- Sex Hormones: Hormones produced by the gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females) that regulate sexual development and reproduction.
- Adrenal Hormones: Hormones produced by the adrenal glands that help regulate stress response, metabolism, and immune function.
- Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): A hormone produced by the parathyroid glands that regulates calcium and phosphate levels in the blood.
- Endocrine Disruptors: Chemicals that interfere with the normal functioning of the endocrine system and can disrupt growth and development.
- Puberty: The stage of development during which sexual maturity is reached and reproductive functions become possible.
- Menopause: The stage in a woman’s life when menstrual periods stop and hormone production decreases.