The endocrine system is a complex network of glands that produce and regulate hormones, which play a crucial role in maintaining various bodily functions such as metabolism, growth, and reproduction. Hormones act as chemical messengers, traveling through the bloodstream to target organs and tissues to control processes like metabolism, growth, and development.
What are Endocrine Disruptors?
Endocrine disruptors are chemicals that interfere with the body’s endocrine system and disrupt the normal regulation of hormones. These disruptors can mimic, block, or interfere with the body’s natural hormones, leading to a variety of health issues. Endocrine disruptors can be found in everyday products such as plastics, pesticides, and personal care products.
How Do Endocrine Disruptors Affect Hormone Regulation?
Endocrine disruptors can impact hormone regulation in several ways. They can mimic natural hormones, leading to overstimulation of target organs and tissues. They can also block hormone receptors, preventing the body from responding to its own hormones properly. Additionally, endocrine disruptors can interfere with hormone production, leading to imbalances in hormone levels.
Health Effects of Endocrine Disruptors
Exposure to endocrine disruptors has been linked to a variety of health issues, including reproductive disorders, hormone-related cancers, metabolic disorders, and developmental abnormalities. Pregnant women, infants, and children are particularly vulnerable to the effects of endocrine disruptors, as these chemicals can impact the development of the endocrine system.
Regulating Exposure to Endocrine Disruptors
Regulating exposure to endocrine disruptors is crucial to protecting public health. Government agencies around the world have implemented regulations to restrict the use of certain endocrine disruptors in consumer products. Individuals can also take steps to reduce their exposure to endocrine disruptors by choosing products that are free of these harmful chemicals.
Summary
The impact of endocrine disruptors on hormone regulation is a significant public health concern. Understanding how these chemicals affect the endocrine system and taking steps to minimize exposure can help protect individuals from the potential health risks associated with endocrine disruptors.
Key Takeaways:
- Endocrine disruptors are environmental chemicals that interfere with the body’s hormone regulation system.
- Common endocrine disruptors include pesticides, plastics, and certain household products.
- Exposure to endocrine disruptors can lead to a variety of health issues, including reproductive problems, cancer, and developmental disorders.
- Pregnant women and children are particularly vulnerable to the effects of endocrine disruptors.
- Reducing exposure to endocrine disruptors can help protect against negative health outcomes.
Key Terms:
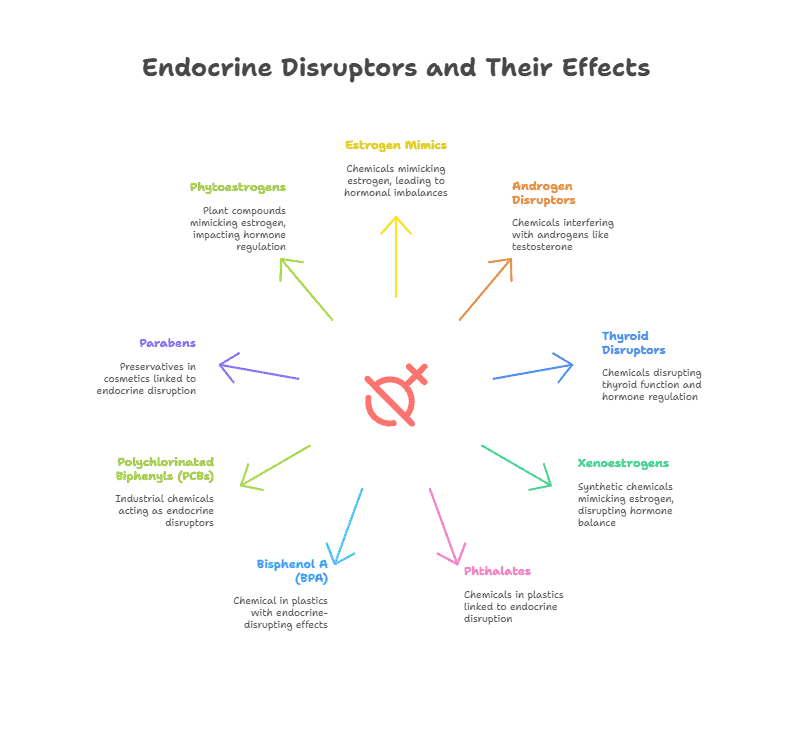
- Endocrine disruptors: Chemicals that can interfere with the body’s endocrine system and disrupt the normal function of hormones.
- Estrogen mimics: Chemicals that mimic the effects of estrogen in the body, potentially leading to hormonal imbalances.
- Androgen disruptors: Chemicals that interfere with the action of androgens, such as testosterone, in the body.
- Thyroid disruptors: Chemicals that disrupt the function of the thyroid gland and can impact hormone regulation.
- Xenoestrogens: Synthetic chemicals that mimic the effects of estrogen in the body, potentially disrupting hormone balance.
- Phthalates: Chemicals commonly used in plastics that have been linked to endocrine disruption.
- Bisphenol A (BPA): A chemical used in the production of plastics that has been shown to have endocrine-disrupting effects.
- Polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs): Industrial chemicals that have been banned but still persist in the environment and can act as endocrine disruptors.
- Parabens: Preservatives commonly used in cosmetics and personal care products that have been linked to endocrine disruption.
- Phytoestrogens: Plant compounds that can mimic the effects of estrogen in the body and impact hormone regulation.