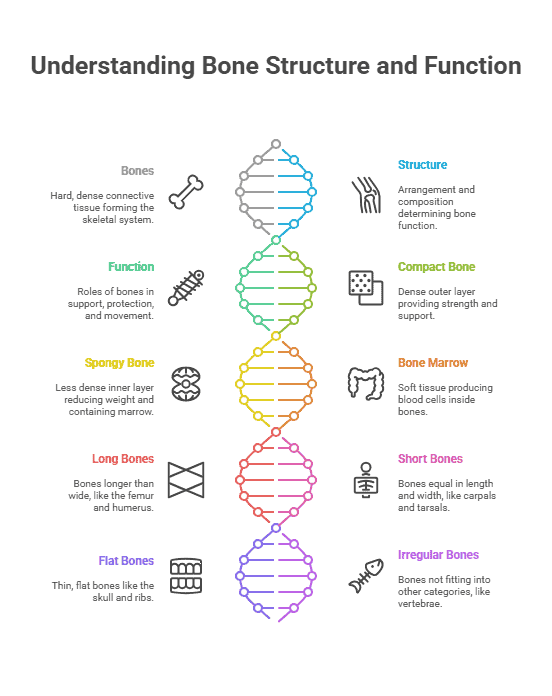
The human skeletal system is made up of different types of bones that work together to provide structure, support, and protection for the body. Understanding the types of bones in the human body is essential for studying anatomy and physiology.
1. Long Bones
Long bones are found in the arms, legs, fingers, and toes. They are characterized by their elongated shape and consist of a shaft (diaphysis) and two ends (epiphyses). Long bones play a crucial role in movement and support.
2. Short Bones
Short bones are cube-shaped and are found in the wrists and ankles. They provide stability and support for the body and help with weight-bearing activities.
3. Flat Bones
Flat bones are thin and flat and are found in the skull, ribs, and shoulder blades. They provide protection for internal organs and serve as attachment points for muscles.
4. Irregular Bones
Irregular bones have complex shapes and are found in the spine and face. They have unique functions and provide support and protection for specific structures in the body.
5. Sesamoid Bones
Sesamoid bones are small, round bones found within tendons, most commonly in the hands, knees, and feet. They help to reduce friction and provide mechanical advantage for movement.
Summary
In summary, the human skeletal system is made up of various types of bones, each with its own unique characteristics and functions. Long bones provide support and movement, short bones offer stability, flat bones protect internal organs, irregular bones have complex shapes and functions, and sesamoid bones reduce friction and enhance movement. Understanding the types of bones in the human body is essential for studying anatomy and physiology.
Key Takeaways:
- Bones are classified into five main types: long bones, short bones, flat bones, irregular bones, and sesamoid bones.
- Long bones are longer than they are wide and are found in the arms and legs.
- Short bones are roughly equal in length and width and are found in the wrists and ankles.
- Flat bones are thin and curved, providing protection to vital organs like the skull and ribs.
- Irregular bones have complex shapes and are found in the spine and face.
- Sesamoid bones are small and round, embedded within tendons to protect them from wear and tear.
Key Terms:
- Long bones: Bones that are longer than they are wide, such as the femur and humerus.
- Short bones: Bones that are approximately equal in length and width, such as the carpals and tarsals.
- Flat bones: Bones that are thin and flat, such as the skull and ribs.
- Irregular bones: Bones that do not fit into any of the other categories due to their unique shape, such as the vertebrae and hip bones.
- Sesamoid bones: Small bones embedded within tendons, such as the patella.