Cartilage is a type of connective tissue that plays a crucial role in the skeletal system. It is a flexible and resilient tissue that provides support and cushioning to the bones of the body. Cartilage is found in various parts of the body, including the joints, ears, nose, and in between the vertebrae of the spine.
Types of Cartilage
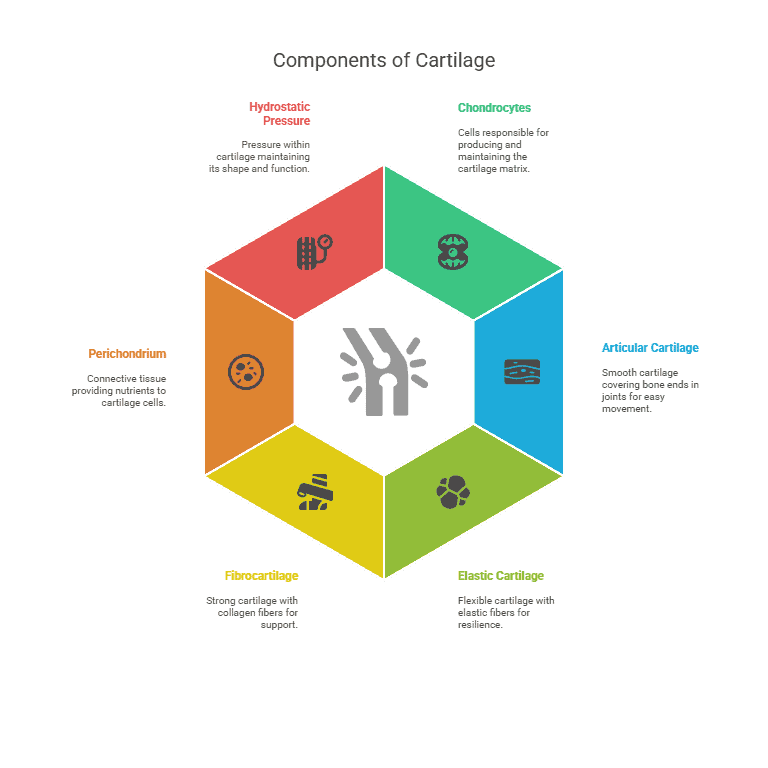
There are three main types of cartilage in the human body: hyaline cartilage, elastic cartilage, and fibrocartilage. Hyaline cartilage is the most common type and is found in the joints, respiratory tract, and at the ends of bones. Elastic cartilage is found in the external ear and epiglottis, providing flexibility and support. Fibrocartilage is found in the intervertebral discs and acts as a shock absorber.
Functions of Cartilage
Cartilage serves several important functions in the skeletal system. It helps to reduce friction between bones at the joints, allowing for smooth movement. Cartilage also absorbs shock and distributes pressure evenly across the joint surfaces, protecting the bones from damage. In addition, cartilage provides structural support to the body, helping to maintain the shape and integrity of various body parts.
Role in Growth and Development
Cartilage plays a crucial role in the growth and development of the skeletal system. During childhood and adolescence, cartilage serves as a template for bone formation. As a child grows, the cartilage in the growth plates of the bones gradually ossifies, or turns into bone, allowing for longitudinal growth. Without cartilage, bones would not be able to grow properly and reach their full size.
Role in Repair and Healing
Cartilage also plays a key role in the repair and healing of injuries in the skeletal system. When a bone is fractured, cartilage forms a soft callus at the site of the injury, providing a temporary scaffold for new bone to grow. Over time, the cartilage is replaced by new bone tissue, allowing the fracture to heal. In conditions such as osteoarthritis, where cartilage wears away over time, the body’s ability to repair and regenerate cartilage is impaired, leading to joint pain and stiffness.
Summary
Cartilage is a vital component of the skeletal system, providing support, cushioning, and flexibility to the bones of the body. It plays a crucial role in growth and development, repair and healing, and overall function of the skeletal system. Understanding the functions and types of cartilage is essential for maintaining healthy bones and joints throughout life.
Key Takeaways:
- Cartilage is a flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the skeletal system.
- It provides support, cushioning, and flexibility to the bones and joints.
- There are three main types of cartilage: hyaline cartilage, fibrocartilage, and elastic cartilage.
- Cartilage does not have a direct blood supply, which affects its ability to repair and regenerate.
- Injuries to cartilage, such as tears or degeneration, can lead to pain and limited mobility.
- Proper nutrition, exercise, and avoiding excessive wear and tear can help maintain healthy cartilage.
Key Terms:
- Cartilage: A firm, flexible connective tissue found in various parts of the body, including the joints and the outer ear.
- Chondrocytes: Cells that produce and maintain the cartilage matrix.
- Articular cartilage: Cartilage that covers the ends of bones in joints, providing a smooth surface for movement.
- Elastic cartilage: Cartilage with a high concentration of elastic fibers, providing flexibility and resilience.
- Fibrocartilage: Cartilage with a high concentration of collagen fibers, providing strength and support.
- Perichondrium: The dense connective tissue that surrounds cartilage and provides nutrients to the cartilage cells.
- Hydrostatic pressure: The pressure within the cartilage that helps maintain its shape and function.