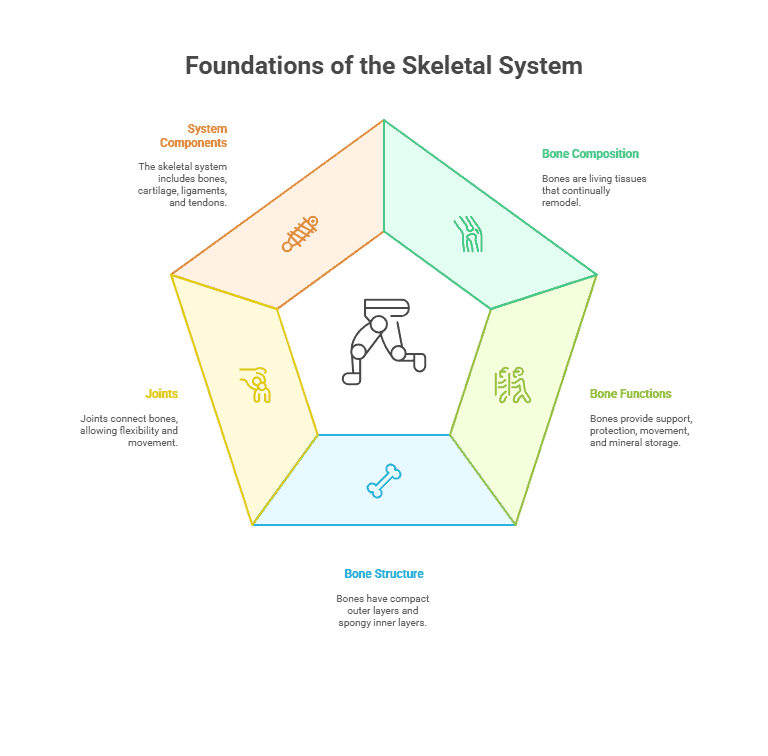
The skeletal system is composed of bones, which provide support, protection, and structure to the body. Bones are made up of a matrix of collagen fibers and mineral deposits, primarily calcium phosphate, which gives them their strength and hardness.
Structure of Bones
Bones are classified into two main types: compact bone and spongy bone. Compact bone is dense and forms the outer layer of bones, while spongy bone is less dense and is found in the inner layers. Both types of bone contain bone marrow, which produces blood cells and stores fat.
Within each bone, there are different types of bone cells that perform specific functions. Osteoblasts are responsible for bone formation, while osteoclasts break down bone tissue. Osteocytes are mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix, and bone lining cells regulate the movement of calcium in and out of the bone.
Function of Bones
Bones have several important functions in the body. They provide support and structure, allowing us to stand upright and move. Bones also protect vital organs, such as the brain and heart, from injury. Additionally, bones store minerals, such as calcium and phosphorus, which are essential for various bodily functions.
Bones are also involved in the production of blood cells through a process called hematopoiesis. Bone marrow, located within the cavities of bones, produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, which are necessary for oxygen transport, immune function, and blood clotting.
Summary
In summary, bones are essential structures in the skeletal system that provide support, protection, and structure to the body. They are composed of compact and spongy bone, contain bone marrow, and are made up of bone cells that perform specific functions. Bones play a critical role in supporting the body, protecting organs, storing minerals, and producing blood cells.
Key Takeaways:
- Bones are composed of living tissue that continually remodels throughout life.
- Bones provide support, protection, movement, and storage of minerals for the body.
- The structure of a bone includes compact bone on the outer layer and spongy bone on the inner layer.
- Bones are connected by joints, which allow for movement and flexibility.
- The skeletal system is made up of bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
Key Terms:
- Bones: Hard, dense connective tissue that makes up the skeletal system.
- Skeletal System: The system of bones and connective tissues that provide support and protection for the body.
- Structure: The arrangement and composition of bones that determine their function.
- Function: The role or purpose of bones in the body, such as support, protection, and movement.
- Compact Bone: Dense outer layer of bone that provides strength and support.
- Spongy Bone: Less dense inner layer of bone that contains bone marrow and helps to reduce weight.
- Bone Marrow: Soft tissue inside bones that produces blood cells.
- Long Bones: Bones that are longer than they are wide, such as the femur and humerus.
- Short Bones: Bones that are approximately equal in length and width, such as the carpals and tarsals.
- Flat Bones: Bones that are thin and flat, such as the skull and ribs.
- Irregular Bones: Bones that do not fit into the categories of long, short, or flat bones, such as the vertebrae and pelvis.