Understanding how bones develop and grow is essential in grasping the importance of the skeletal system in the human body. Bones are the structural framework that supports our body, protects our organs, and allows us to move. The process of bone development and growth is a complex and fascinating journey that begins before birth and continues throughout our lives.
Embryonic Development
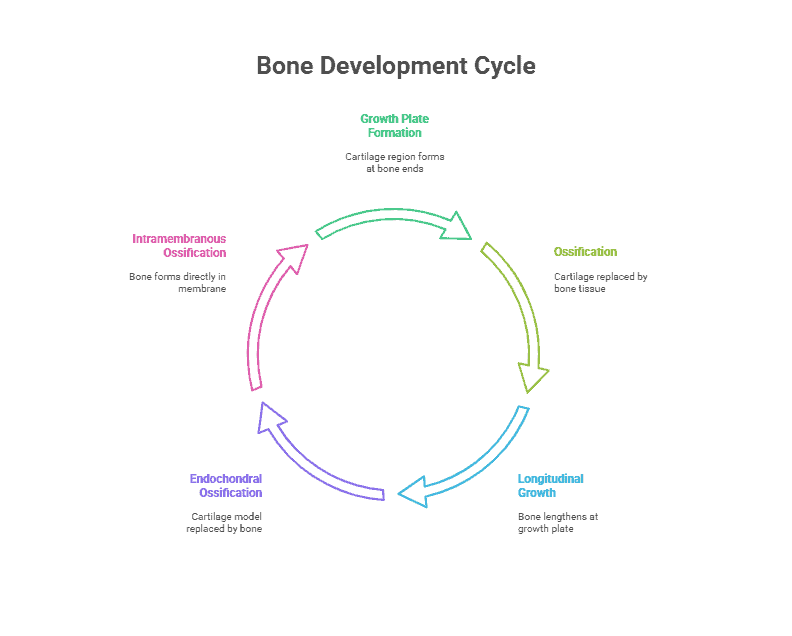
During embryonic development, the skeletal system starts as cartilage, a flexible and strong connective tissue. Over time, this cartilage is replaced by bone in a process known as ossification. Ossification occurs in two main ways: intramembranous ossification, which forms flat bones like the skull, and endochondral ossification, which forms long bones like the femur.
Postnatal Growth
After birth, bones continue to grow and develop. This growth is primarily driven by the activity of growth plates, also known as epiphyseal plates, located at the ends of long bones. These growth plates are made up of cartilage cells that divide and multiply, pushing the bone to lengthen. As a person reaches adulthood, these growth plates close, and bone growth stops.
Factors Affecting Bone Growth
Several factors influence bone development and growth. Nutrition plays a crucial role, as bones require adequate amounts of calcium, phosphorus, and other minerals to grow and maintain their strength. Hormones such as growth hormone and sex hormones also play a significant role in bone development. Physical activity, particularly weight-bearing exercises, is essential for stimulating bone growth and maintaining bone density.
Summary
In summary, bone development and growth are intricate processes that begin in the embryonic stage and continue throughout life. Understanding these processes is essential for maintaining healthy bones and overall skeletal health. Factors such as nutrition, hormones, and physical activity all play a crucial role in supporting bone growth and development.
Key Takeaways:
- Bone development begins in the womb and continues throughout childhood and adolescence.
- Bone growth is influenced by genetics, nutrition, hormones, and physical activity.
- The epiphyseal plate, also known as the growth plate, is responsible for longitudinal bone growth.
- Bone remodeling is a lifelong process that involves the removal of old bone and the formation of new bone.
- Proper nutrition, exercise, and medical care are important for healthy bone development and growth.
Key Terms:
- Bone Development: The process by which bones grow and mature over time.
- Growth Plate: A region of cartilage at the end of a long bone where growth occurs.
- Ossification: The process of bone formation, where cartilage is replaced by bone tissue.
- Epiphyseal Plate: Another term for growth plate, where longitudinal bone growth occurs.
- Endochondral Ossification: The process of bone formation in which a cartilage model is gradually replaced by bone tissue.
- Intramembranous Ossification: The process of bone formation in which bone tissue is formed directly within a membrane of connective tissue.