Understanding the basics of the respiratory system is crucial for maintaining good health and well-being. One key aspect of this system is pulmonary circulation and oxygen transport. This process involves the movement of blood through the lungs to pick up oxygen and release carbon dioxide. Let’s delve into this topic to gain a better understanding of how our bodies function.
Pulmonary Circulation
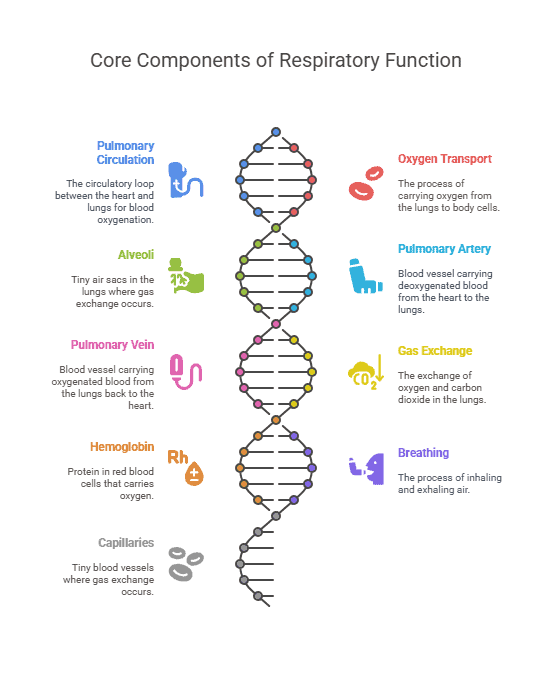
Pulmonary circulation refers to the flow of blood between the heart and the lungs. When oxygen-poor blood returns to the heart from the body, it is pumped to the lungs through the pulmonary arteries. In the lungs, the blood picks up oxygen and releases carbon dioxide through the process of respiration. The oxygen-rich blood then returns to the heart via the pulmonary veins to be circulated to the rest of the body.
Oxygen Transport
Oxygen transport is the process by which oxygen is carried from the lungs to the body’s tissues. In the lungs, oxygen binds to hemoglobin, a protein in red blood cells, forming oxyhemoglobin. This oxygenated blood is then pumped by the heart to all parts of the body through the systemic circulation. Once the oxygen reaches the tissues, it is released from hemoglobin and used for cellular respiration to produce energy.
Carbon dioxide, a waste product of cellular respiration, is carried back to the lungs by the blood. In the lungs, carbon dioxide is exchanged for oxygen and removed from the body through exhalation. This process ensures that the body receives a constant supply of oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide efficiently.
Summary
In summary, pulmonary circulation and oxygen transport are essential processes in the respiratory system that ensure the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen and eliminates carbon dioxide. Understanding how blood is circulated between the heart and lungs, and how oxygen is transported to the tissues, helps us appreciate the intricate workings of our respiratory system. By maintaining a healthy respiratory system, we can support our overall well-being and vitality.
Key Takeaways:
- Pulmonary circulation is the movement of blood from the heart to the lungs and back again for oxygenation.
- The main function of the pulmonary circulation is to exchange carbon dioxide for oxygen in the blood.
- Oxygen is transported in the blood primarily bound to hemoglobin in red blood cells.
- Factors that affect oxygen transport include altitude, exercise, and certain medical conditions.
- Understanding pulmonary circulation and oxygen transport is crucial for maintaining overall respiratory health.
Key Terms:
- Pulmonary circulation: The circulation of blood from the heart to the lungs and back to the heart.
- Oxygen transport: The process of carrying oxygen from the lungs to the cells of the body.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
- Pulmonary artery: Blood vessel that carries deoxygenated blood from the heart to the lungs.
- Pulmonary vein: Blood vessel that carries oxygenated blood from the lungs back to the heart.
- Gas exchange: The process of oxygen and carbon dioxide moving between the alveoli and the blood.
- Hemoglobin: Protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen.
- Respiratory system: The organs and structures involved in breathing and gas exchange.
- Breathing: The process of inhaling and exhaling air.
- Capillaries: Tiny blood vessels where gas exchange occurs.