Understanding how breathing works is essential for maintaining good respiratory health. The process of breathing, also known as ventilation, involves the movement of air into and out of the lungs to facilitate the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide.
Mechanics of Breathing
During inhalation, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, while the intercostal muscles between the ribs expand the chest cavity. This creates negative pressure in the lungs, causing air to rush in. Exhalation occurs when the diaphragm relaxes and moves upward, and the intercostal muscles contract, reducing the volume of the chest cavity and pushing air out of the lungs.
Gas Exchange
Once air enters the lungs, it travels to the alveoli, tiny air sacs where gas exchange takes place. Oxygen from the air passes through the thin walls of the alveoli into the bloodstream, while carbon dioxide moves from the blood into the alveoli to be exhaled.
Regulation of Breathing
The respiratory center in the brainstem controls the rate and depth of breathing based on the body’s needs. Factors such as carbon dioxide levels, oxygen levels, and pH in the blood influence the respiratory center to adjust breathing accordingly.
Respiratory Disorders
Disruptions in the physiology of breathing can lead to respiratory disorders such as asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and pneumonia. Understanding the normal functioning of the respiratory system is crucial for managing and treating these conditions.
Summary
The physiology of breathing involves the mechanics of inhalation and exhalation, gas exchange in the alveoli, regulation of breathing by the respiratory center, and the impact of respiratory disorders on lung function. By understanding these concepts, individuals can take steps to maintain healthy lungs and seek appropriate medical care when needed.
Key Takeaways:
- The primary function of the respiratory system is to bring oxygen into the body and expel carbon dioxide.
- Breathing is controlled by the diaphragm and intercostal muscles, which work together to expand and contract the chest cavity.
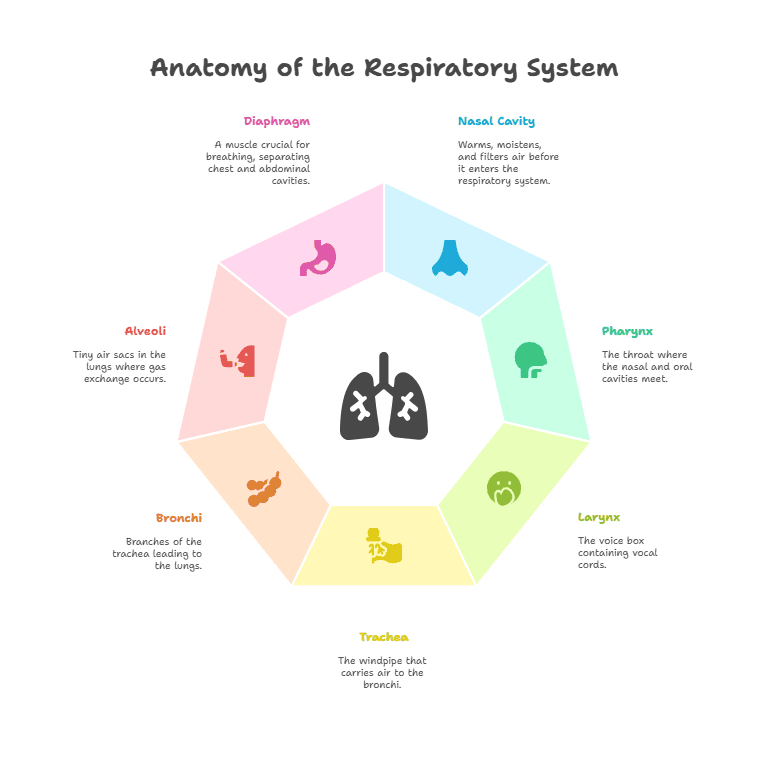
- The process of breathing involves inhaling air through the nose or mouth, passing it through the trachea, and into the lungs.
- In the lungs, oxygen is transferred to the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is removed from the body through exhalation.
- Respiratory rate and depth can be influenced by factors such as exercise, emotions, and medical conditions.
Key Terms:
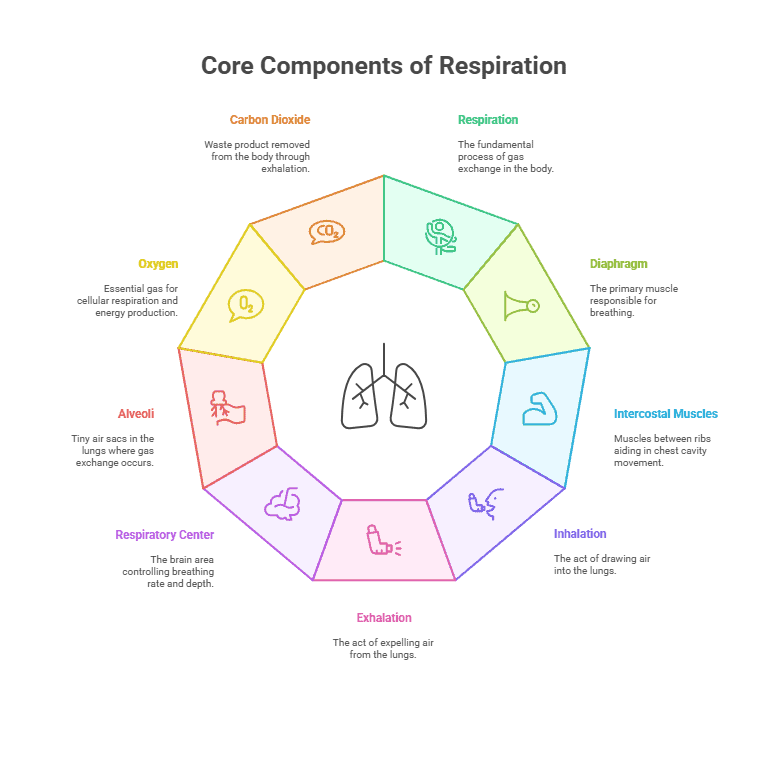
- Respiration: The process of exchanging gases between the atmosphere and the body’s cells.
- Diaphragm: A dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs that plays a key role in breathing.
- Intercostal Muscles: Muscles located between the ribs that help with expanding and contracting the chest cavity during breathing.
- Inhalation: The process of breathing in air, which involves the diaphragm contracting and the chest cavity expanding.
- Exhalation: The process of breathing out air, which involves the diaphragm relaxing and the chest cavity contracting.
- Respiratory Center: The area of the brain that controls the rate and depth of breathing.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
- Oxygen: A gas that is essential for cellular respiration and energy production in the body.
- Carbon Dioxide: A waste product of cellular respiration that is removed from the body through exhalation.