The respiratory system is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide from the body. It is essential for our survival as oxygen is needed for cells to function correctly and produce energy. The respiratory system also helps to regulate the body’s pH levels and plays a role in the sense of smell.
Organs of the Respiratory System
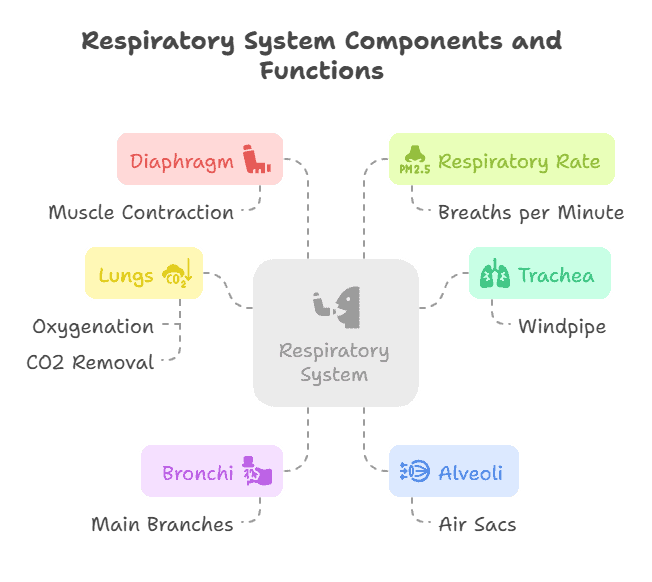
The respiratory system comprises several organs, including the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs. Each of these organs plays a specific role in the process of breathing and gas exchange.
Nose and Pharynx
The nose is the primary entry point for air into the respiratory system. It filters, warms, and moistens the air before it enters the pharynx, which is a passageway for both air and food.
Larynx and Trachea
The larynx, or voice box, contains the vocal cords and is responsible for producing sound. It also serves as a passageway for air to travel from the pharynx to the trachea. The trachea, or windpipe, carries air to the lungs and is lined with cilia that help to filter out foreign particles.
Bronchi and Lungs
The trachea branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. The bronchi further divide into smaller tubes called bronchioles, which end in clusters of air sacs called alveoli. The alveoli are where gas exchange takes place, with oxygen moving into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide being expelled from the body.
Functions of the Respiratory System
In addition to gas exchange, the respiratory system also helps to regulate the body’s pH levels by controlling the amount of carbon dioxide in the blood. It also plays a role in the sense of smell, as air containing odor molecules passes through the nasal cavity and stimulates olfactory receptors.
Summary
The respiratory system is essential for the body’s survival, as it is responsible for taking in oxygen and expelling carbon dioxide. It is made up of organs such as the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs, each playing a specific role in the process of breathing and gas exchange. In addition to these functions, the respiratory system also helps to regulate the body’s pH levels and plays a role in the sense of smell.
Key Takeaways:
- The respiratory system is responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and expelling carbon dioxide.
- Key organs of the respiratory system include the nose, trachea, lungs, and diaphragm.
- Respiration involves both inhalation (breathing in) and exhalation (breathing out).
- The alveoli in the lungs are where gas exchange takes place, with oxygen entering the bloodstream and carbon dioxide being removed.
- Various factors such as smoking, pollution, and respiratory infections can impact the health of the respiratory system.
Key Terms:
- Respiratory System: The system responsible for bringing oxygen into the body and removing carbon dioxide.
- Trachea: The windpipe that connects the larynx to the bronchi.
- Bronchi: The two main branches that lead from the trachea to the lungs.
- Lungs: The organs responsible for oxygenating the blood and removing carbon dioxide.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange occurs.
- Diaphragm: The muscle responsible for breathing, contracting to expand the lungs and inhale air.
- Respiratory Rate: The number of breaths taken per minute.