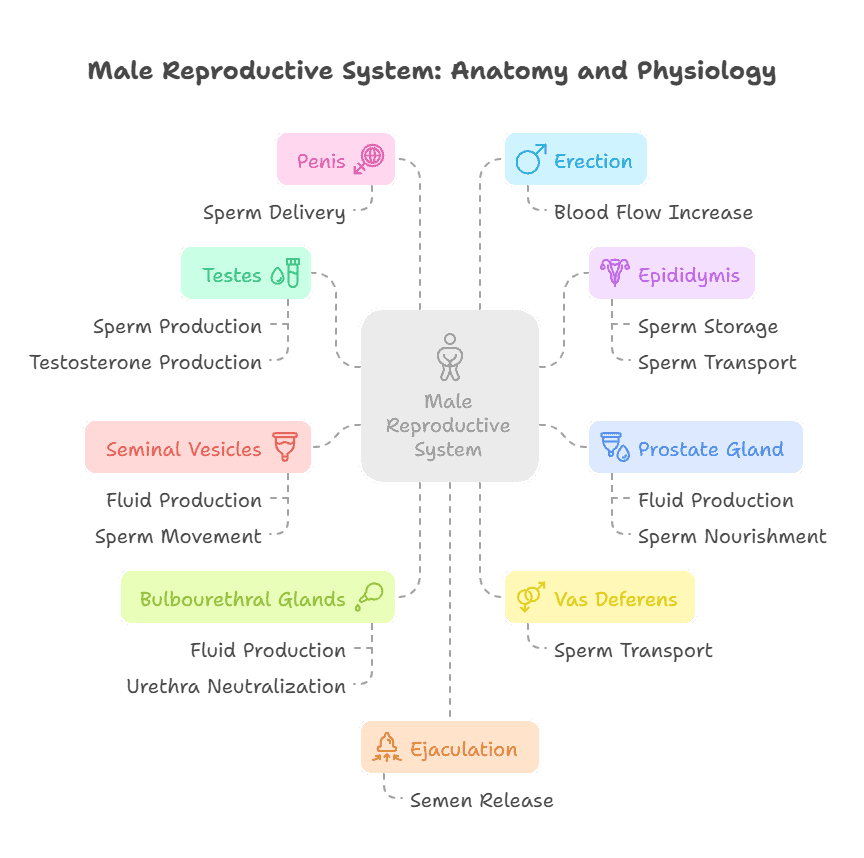
The male reproductive system is a complex and intricate system responsible for the production and delivery of sperm, as well as the production of hormones that regulate reproductive functions. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the male reproductive system is crucial for understanding male fertility, sexual function, and overall health.
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system consists of several key organs, including the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and seminal vesicles. The testes are responsible for producing sperm and the hormone testosterone, while the epididymis stores and transports sperm. The vas deferens carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra, where it is mixed with fluids from the prostate gland and seminal vesicles to form semen.
Physiology of the Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system is regulated by a complex interplay of hormones, including testosterone, luteinizing hormone (LH), and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH). Testosterone is crucial for sperm production, sexual function, and the development of secondary sexual characteristics. LH and FSH help regulate testosterone production and sperm maturation.
Reproductive Functions
The primary function of the male reproductive system is the production and delivery of sperm for fertilization of a female egg. In addition to sperm production, the male reproductive system also plays a role in sexual arousal and ejaculation. The prostate gland and seminal vesicles produce fluids that nourish and protect sperm during ejaculation.
Importance of Male Reproductive Health
Maintaining the health of the male reproductive system is essential for overall health and well-being. Regular physical exams, healthy lifestyle choices, and proper hygiene are important for preventing reproductive system disorders and promoting fertility.
Summary
In summary, the male reproductive system is a complex system responsible for the production and delivery of sperm, as well as the regulation of reproductive functions through the production of hormones. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the male reproductive system is crucial for maintaining reproductive health and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The male reproductive system includes the testes, vas deferens, prostate gland, and penis.
- The primary function of the male reproductive system is to produce and deliver sperm to fertilize an egg.
- Sperm is produced in the testes and stored in the epididymis before being ejaculated through the vas deferens.
- The prostate gland produces a fluid that mixes with sperm to create semen.
- The penis is responsible for delivering semen into the female reproductive system during intercourse.
- Hormones such as testosterone play a crucial role in the development and function of the male reproductive system.
Key Terms:
- Male Reproductive System: The set of organs involved in the production of sperm and the transfer of sperm to the female reproductive system.
- Testes: The male reproductive organs that produce sperm and testosterone.
- Epididymis: A coiled tube that stores sperm and transports it from the testes to the vas deferens.
- Vas Deferens: The tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra.
- Prostate Gland: A gland that produces a fluid that helps nourish and protect sperm.
- Seminal Vesicles: Glands that produce a fluid that helps sperm move and survive in the female reproductive system.
- Bulbourethral Glands: Glands that produce a fluid that helps neutralize acidity in the urethra and lubricate the tip of the penis.
- Penis: The male external organ of reproduction that delivers sperm to the female reproductive system.
- Erection: The process of the penis becoming enlarged and rigid due to increased blood flow.
- Ejaculation: The release of semen from the male reproductive system.