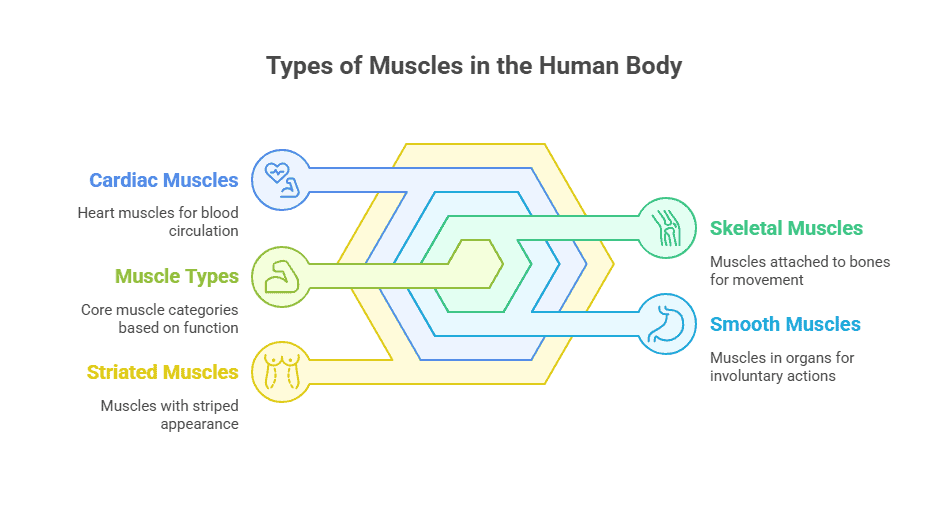
When we think of muscles, we often picture the ones that we can see and feel, like the biceps or quadriceps. However, the human body is made up of three different types of muscles, each with their own unique characteristics and functions. Understanding these types of muscles is essential for anyone studying anatomy or interested in how the body moves and functions.
Skeletal Muscles
Skeletal muscles are the muscles that we can see and feel. They are attached to bones by tendons and are responsible for movement. These muscles are under voluntary control, meaning that we can choose to contract them to perform specific actions. Skeletal muscles work in pairs, with one muscle contracting while the other relaxes to produce movement. These muscles are striated, meaning they have a striped appearance under a microscope.
Smooth Muscles
Smooth muscles are found in the walls of internal organs, such as the stomach, intestines, and blood vessels. These muscles are responsible for involuntary movements, such as the contractions of the stomach during digestion or the dilation of blood vessels. Smooth muscles are not striated like skeletal muscles, which is why they appear smooth under a microscope.
Cardiac Muscles
Cardiac muscles are unique to the heart and are responsible for pumping blood throughout the body. These muscles are also involuntary, meaning that we do not have conscious control over their contractions. Cardiac muscles are striated like skeletal muscles, but they are branched and interconnected to allow for the coordinated contraction of the heart.
Summary
In conclusion, the human body is composed of three types of muscles: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac. Skeletal muscles are responsible for voluntary movements and are attached to bones, while smooth muscles control involuntary movements in internal organs. Cardiac muscles are specific to the heart and play a vital role in pumping blood throughout the body. Understanding the differences between these types of muscles is essential for grasping the complexities of the human body and how it functions.
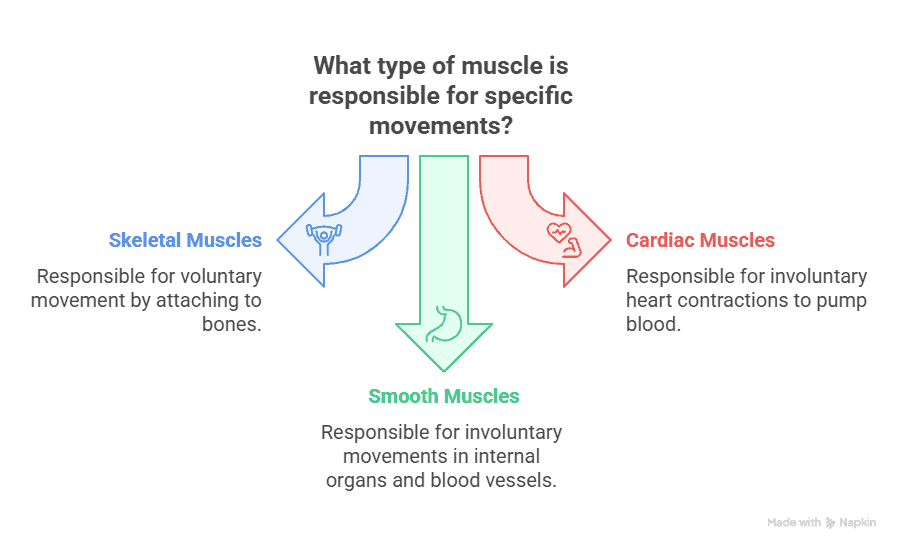
Key Takeaways:
- Skeletal muscles are attached to bones and are responsible for voluntary movement.
- Cardiac muscles are found in the heart and are responsible for involuntary contractions to pump blood.
- Smooth muscles are found in internal organs and blood vessels, and are responsible for involuntary movements.
- Muscles work in pairs to produce movement – one muscle contracts while the other relaxes.
- Muscles can only pull, not push, so they work in opposing pairs to create movement in different directions.
Key Terms:
- Skeletal Muscles: Muscles that are attached to bones and produce movement by contracting and relaxing.
- Smooth Muscles: Muscles that are found in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels, responsible for involuntary movements.
- Cardiac Muscles: Muscles found in the heart, responsible for pumping blood throughout the body.
- Striated Muscles: Muscles that have a striped appearance due to the arrangement of their fibers, includes skeletal and cardiac muscles.
- Involuntary Muscles: Muscles that are not under conscious control, such as smooth and cardiac muscles.
- Voluntary Muscles: Muscles that are under conscious control, such as skeletal muscles.