When it comes to understanding how our muscles work, one crucial area to explore is the neuromuscular junction. This junction is where nerves communicate with muscles, allowing for the coordination of movement throughout our bodies.
What is the Neuromuscular Junction?
The neuromuscular junction is a specialized synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber. It is the point where the nervous system controls muscle contraction by sending signals from the brain to the muscle fibers.
How Does it Work?
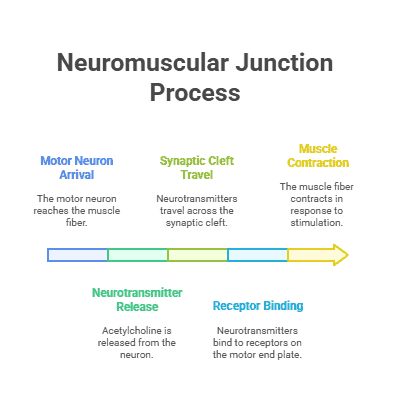
When a signal is sent from the brain to a muscle, it travels down the motor neuron and reaches the neuromuscular junction. At this junction, the signal triggers the release of neurotransmitters, specifically acetylcholine, into the synaptic cleft. These neurotransmitters then bind to receptors on the muscle fiber, causing a series of chemical reactions that ultimately lead to muscle contraction.
The Role of Acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is a key neurotransmitter in the neuromuscular junction. It is responsible for transmitting the signal from the motor neuron to the muscle fiber, leading to the initiation of muscle contraction. Without acetylcholine, the communication between nerves and muscles would not be possible.
Importance of the Neuromuscular Junction
The neuromuscular junction is essential for proper muscle function and movement. Without this connection between nerves and muscles, our bodies would not be able to perform simple actions such as walking, talking, or even breathing. Understanding how this junction works can provide valuable insight into the intricate processes that govern our muscular system.
Summary
In summary, the neuromuscular junction is a vital component of the muscular system, where nerves meet muscles to coordinate movement. It relies on the release of acetylcholine neurotransmitters to signal muscle contraction, playing a crucial role in our everyday activities. By exploring this junction, we can gain a better understanding of how our muscles function and the importance of proper communication between nerves and muscles.
Key Takeaways:
- The neuromuscular junction is the point where a motor neuron meets a muscle fiber
- Neurotransmitters like acetylcholine are released from the motor neuron to stimulate muscle contraction
- The synaptic cleft is the gap between the motor neuron and muscle fiber where neurotransmitters travel
- The motor end plate on the muscle fiber contains receptors for neurotransmitters
- Understanding the neuromuscular junction is crucial for understanding how muscles contract
Key Terms:
- Neuromuscular Junction: The point of contact between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber
- Motor Neuron: Nerve cell that controls muscle movement
- Acetylcholine: Neurotransmitter released by motor neurons to stimulate muscle contraction
- Synaptic Cleft: Gap between the motor neuron and muscle fiber where neurotransmitters are released
- Motor End Plate: Specialized region of muscle fiber membrane that receives neurotransmitters
- Neurotransmitter: Chemical messenger that transmits signals between neurons and muscles