Our digestive system is a complex network of organs and processes that work together to break down the food we eat into nutrients that our bodies can absorb and use for energy. One often overlooked but crucial component of this system is the gut microbiota.
What is Gut Microbiota?
Gut microbiota, also known as gut flora or gut bacteria, are the trillions of microorganisms that live in our digestive tract. These microorganisms include bacteria, viruses, fungi, and other microbes that play a vital role in our overall health and well-being.
Role in Digestion
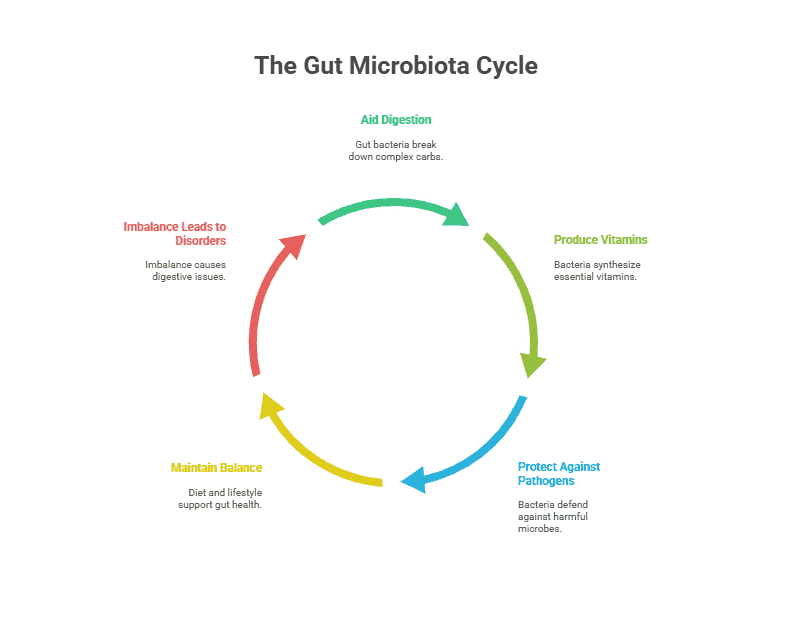
One of the key roles of gut microbiota is to aid in the digestion of food. These microorganisms help break down complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats that our bodies are unable to digest on their own. They also help produce essential vitamins and nutrients that our bodies need to function properly.
Additionally, gut microbiota help maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut, which is essential for proper digestion and overall health. Imbalances in gut bacteria have been linked to a variety of health issues, including digestive disorders, obesity, and autoimmune diseases.
Impact on Immune System
Our gut microbiota also play a crucial role in supporting our immune system. These microorganisms help regulate the immune response, protect against harmful pathogens, and promote the production of antibodies that fight off infections and diseases.
Factors Affecting Gut Microbiota
Several factors can impact the composition and diversity of gut microbiota, including diet, lifestyle, medications, and environmental factors. A diet high in processed foods and low in fiber, for example, can lead to an imbalance in gut bacteria, while a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can promote a healthy gut microbiota.
Summary
In summary, gut microbiota play a crucial role in the digestion process by helping break down food, produce essential nutrients, and maintain a healthy balance of bacteria in the gut. These microorganisms also support our immune system and overall health. Factors such as diet, lifestyle, and medications can impact the composition of gut microbiota, highlighting the importance of maintaining a healthy gut microbiota for optimal digestion and overall well-being.
Key Takeaways:
- The gut microbiota plays a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients in the digestive system.
- Gut bacteria help break down complex carbohydrates, produce vitamins, and protect against harmful pathogens.
- An imbalance in gut microbiota can lead to digestive disorders, such as irritable bowel syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease.
- Diet and lifestyle factors, such as high fiber intake and probiotic consumption, can help maintain a healthy gut microbiota.
- Further research is needed to fully understand the complex interactions between gut microbiota and digestion.
Key Terms:
- Gut microbiota: The community of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract.
- Digestion: The process of breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and used by the body.
- Probiotics: Live bacteria and yeasts that are good for your digestive system.
- Fermentation: The metabolic process that produces chemical changes in organic substrates through the action of enzymes.
- Prebiotics: Non-digestible fiber compounds that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Dysbiosis: An imbalance in the gut microbiota that can lead to health problems.