The human reproductive system is a complex network of organs and hormones that work together to facilitate the creation of new life. It is essential for the survival of our species and plays a crucial role in the continuation of the human race.
Anatomy of the Reproductive System
The reproductive system is divided into two main categories: the male reproductive system and the female reproductive system. Each system contains specific organs that are responsible for producing, storing, and releasing gametes (sperm in males and eggs in females) as well as hormones that regulate the reproductive process.
Male Reproductive System
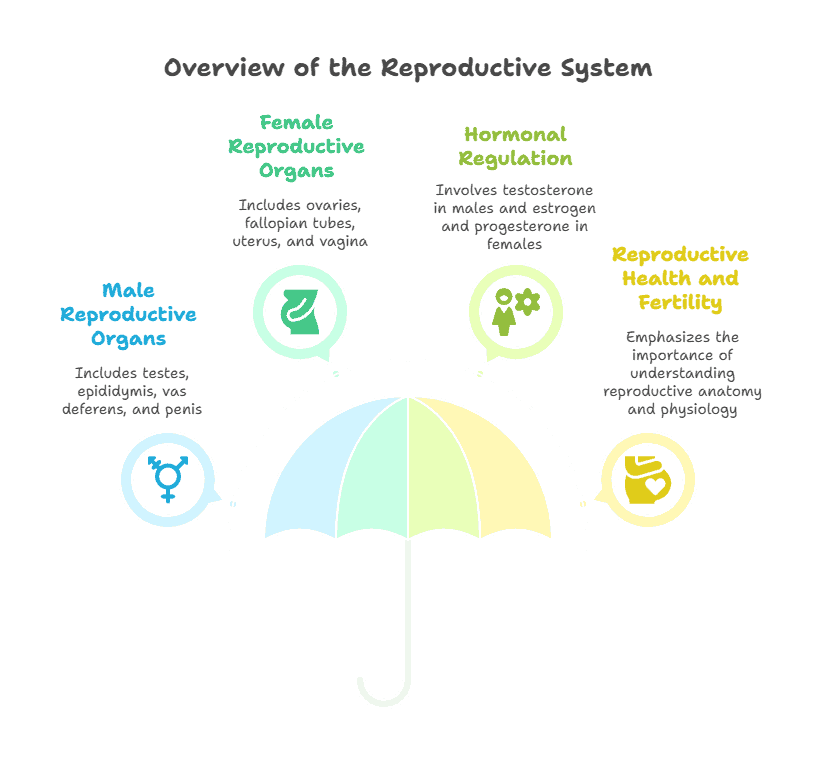
The male reproductive system consists of organs such as the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, prostate gland, and penis. These organs work together to produce and deliver sperm to the female reproductive system during sexual intercourse.
Female Reproductive System
The female reproductive system includes organs like the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and vagina. These organs are responsible for producing eggs, providing a suitable environment for fertilization and implantation, and supporting the development of a fetus during pregnancy.
Physiology of the Reproductive System
The reproductive system is regulated by a complex interplay of hormones produced by the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and gonads (testes in males and ovaries in females). These hormones control the menstrual cycle in females, sperm production in males, and various other reproductive functions.
Reproductive Process
The reproductive process begins with the release of hormones that stimulate the production of gametes and prepare the body for fertilization. In females, this process involves the monthly ovulation of an egg, while in males, it includes the continuous production of sperm.
Fertilization and Pregnancy
Once an egg is fertilized by sperm, it implants in the uterus and begins to develop into a fetus. The female body undergoes numerous changes to support the growth and development of the fetus, including an increase in hormone levels and changes in the reproductive organs.
Summary
The reproductive system is a vital component of human biology, responsible for the creation of new life through the production and delivery of gametes. Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the reproductive system is crucial for comprehending how our bodies function and how we can support our reproductive health.
Key Takeaways:
- The reproductive system is essential for the production of offspring and continuation of the species.
- Key organs of the male reproductive system include the testes, epididymis, vas deferens, and penis.
- Key organs of the female reproductive system include the ovaries, fallopian tubes, uterus, and vagina.
- The reproductive system is regulated by hormones such as testosterone in males and estrogen and progesterone in females.
- Understanding the anatomy and physiology of the reproductive system is important for reproductive health and fertility.
Key Terms:
- Reproductive System: The system of organs involved in producing offspring.
- Anatomy: The structure and organization of body parts.
- Physiology: The study of how body parts function.
- Gonads: Organs that produce gametes (sperm and eggs) and sex hormones.
- Testes: Male gonads that produce sperm and testosterone.
- Ovaries: Female gonads that produce eggs and estrogen.
- Uterus: Organ where a fertilized egg implants and develops into a fetus.
- Fallopian Tubes: Tubes that transport eggs from the ovaries to the uterus.
- Vas Deferens: Tube that transports sperm from the testes to the urethra.
- Menstrual Cycle: Monthly cycle of changes in the female reproductive system.