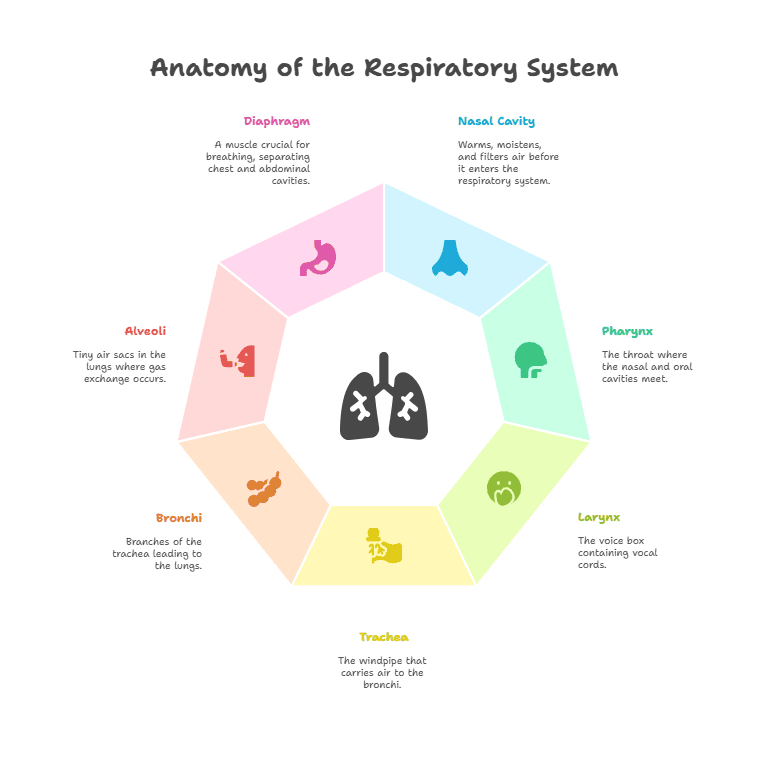
The respiratory system consists of several organs that work together to ensure the body receives an adequate supply of oxygen and removes waste gases.
Nose and Nasal Cavity
The respiratory system begins with the nose and nasal cavity, where air is taken in and filtered before reaching the lungs. The nose hairs and mucous membranes help to trap dust and other particles, preventing them from entering the respiratory tract.
Pharynx and Larynx
After passing through the nasal cavity, air travels through the pharynx and larynx. The pharynx is a passage that connects the nasal cavity to the larynx, while the larynx contains the vocal cords and helps with speech production.
Trachea and Bronchi
The trachea, or windpipe, carries air from the larynx to the lungs. It branches into two bronchi, one leading to each lung. The bronchi further divide into smaller bronchioles, which eventually reach the alveoli in the lungs.
Lungs and Alveoli
The lungs are the primary organs of the respiratory system, responsible for the exchange of gases. Within the lungs, there are millions of tiny air sacs called alveoli, where oxygen from the air is absorbed into the bloodstream and carbon dioxide is released for exhalation.
Diaphragm and Intercostal Muscles
The diaphragm is a dome-shaped muscle located below the lungs that helps with breathing. When we inhale, the diaphragm contracts and moves downward, creating space for the lungs to expand. The intercostal muscles between the ribs also play a role in expanding and contracting the chest cavity during breathing.
Summary
The respiratory system is a complex network of organs and muscles that work together to ensure the body receives oxygen and removes carbon dioxide. From the nose and nasal cavity to the lungs and alveoli, each part of the respiratory system plays a critical role in the process of breathing and gas exchange.
Key Takeaways:
- The respiratory system is responsible for the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the body.
- The main organs of the respiratory system include the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi, and lungs.
- The lungs are the primary organs of respiration, where oxygen is taken in and carbon dioxide is expelled.
- The diaphragm plays a key role in the process of breathing by contracting and relaxing to expand and contract the lungs.
- Respiratory disorders such as asthma, COPD, and pneumonia can affect the function of the respiratory system.
Key Terms:
- Respiratory System: The organs and structures in the body responsible for breathing and gas exchange.
- Nasal Cavity: The space inside the nose where air is warmed, moistened, and filtered before entering the respiratory system.
- Pharynx: The throat, where the nasal cavity and oral cavity meet.
- Larynx: The voice box, containing the vocal cords and located just below the pharynx.
- Trachea: The windpipe, a tube that carries air from the larynx to the bronchi.
- Bronchi: Two branches of the trachea that lead to the lungs.
- Alveoli: Tiny air sacs in the lungs where gas exchange takes place.
- Diaphragm: A muscle that separates the chest cavity from the abdominal cavity and plays a crucial role in breathing.